| Cellular Respiration Review |
1. Most eukaryotic cells produce only about ___________ ATP Molecules per Glucose Molecule.
2. What is the process by which glucose is converted to pyruvic acid? ________________________________________
3. At the beginning of aerobic respiration, pyruvic acid bonds to a molecule called ______________________________________ to form Acetyl CoA.
4. The breakdown of pyruvic acid in the presence of oxygen is called ______________________________ _______________________.
5. With every completion of the Krebs Cycle, how many ATP Molecules are made? ________________
6. What is the waste product of the Krebs Cycle? _____________________________________________.
7. The conversion of pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and ethanol is called ___________________________________ _____________________________________________.
8. The release of energy from food molecules in the absence of oxygen is ______________________________________ _________________________________________________________.
9. What is the byproduct of the electron transport Chain?_______________________________________________.
10. How efficient is Anaerobic Respiration? __________% Aerobic Respiration? ____________%
11. What is the first pathway of cellular respiration called? ________________________________________________
12.What is the location of Glycolysis? _______________________________________________________
13. What is the scientific unit of Energy? ________________________________________________
14. What do you call cellular respiration in the presence of oxygen? _______________________________________ _________________________________________________________.
15. Yeast produces ______________________________ and _______________________________ in the process known as ____________________________________ ___________________________________________.
16. In cellular respiration, glycolysis proceeds the _______________________________ ___________________________.
17. In cellular respiration, more energy is transferred in the ___________________________ ________________________ _________________________________ than in any other step.
18. Glucose molecules are converted into _______________________________ _______________________ molecules in the process of glycolysis.
19. What is the location of the electron transport chain in prokaryotes? ________________ _______________________.
20. The processes of glycolysis and the anaerobic pathways is called ___________________________________.
21. What is the product of acetyl CoA and oxaloacetic acid? _________________ ___________________
22. What molecule is the electron acceptor of glycolysis? _________________________________________
23. The breakdown of organic compounds to produce ATP is known as ____________________________________ ________________________-_______________________________.
24. Glycolysis begins with glucose and produces ______________________________ _________________________.
25. An important molecule generated by both lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation is ______________________________.
26. In the first step of aerobic respiration, pyruvic acid from glycolysis produces CO2, NADH, H+, and _________________________________ _____________________________________.
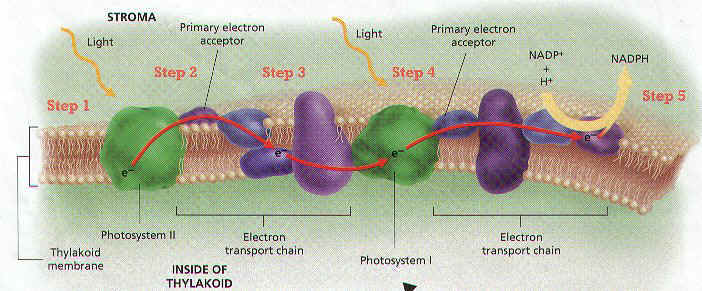
27. The electron transport chain is driven by two products of the Krebs Cycle – ______________________ and ___________________________.
28. What happens to electrons as they are transported along the electron transport chain? _________________________________________________________________
29. The energy efficiency of aerobic respiration (including glycolysis) is approximately ______________ __________________________________________________.
30. Where in the mitochondria do the reactions of the Krebs cycle occur? _____________________________ ___________________________________________________________
31. Where in the mitochondria is the electron transport chain located? _____________________________ __________________________________________________
32. In alcoholic fermentation, ethyl alcohol is produced from _______________________________ ______________________________________.
33. ____________________________________, and _______________________________ supply electrons and protons to the electron transport chain.
34. Cellular respiration takes place in Two Stages: _______________________________________, then ________________________________________ ________________________________.
35. Water is an end product in the ________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________.
36. In cellular respiration, a two-carbon molecule combines with a four-carbon molecule to form citric acid as part of the _____________________________________________________________________________________.
37. When glycolysis occurs, a molecule of glucose is ___________________________________________.
38. The name of the process that takes place when organic compounds are broken down in the absence of oxygen is _____________________________________________ or _______________________________________.
39. Energetic electrons that provide the energy for the production of most of a cell’s ATP are carried to the electron transport chain by _______________________________ and __________________________________________.
40. _______________________________________ is a biochemical pathway of cellular respiration that is anaerobic.
41. Glucose is split into smaller molecules during the biochemical pathway called __________________________________.
42. In the absence of oxygen, instead of oxidative respiration following glycolysis, glycolysis is followed by ______________________________________________________.
43. During fermentation, either ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide or _______________________________________ is formed.
DIRECTIONS: Answer the questions below as completely and as thoroughly as possible. Answer the question in essay form (not outline form), using complete sentences. You may use diagrams to supplement your answers, but a diagram alone without appropriate discussion is inadequate.
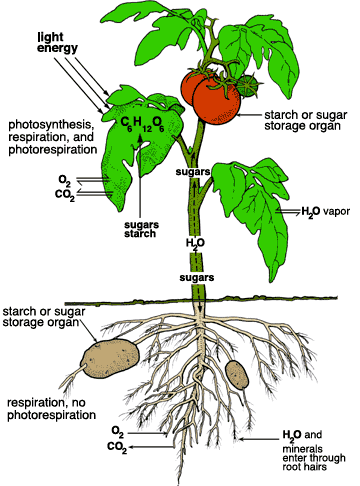
1. How does aerobic respiration ultimately depend on photosynthesis?
2. Explain the role of oxaloacetic acid with respect to the cyclical nature of the Krebs cycle.
3. Glycolysis produces only 3.5% of the energy that would be produced if an equal quantity of glucose were completely oxidized. What has happened to the remaining energy in the glucose?
4. Why do most cells produce fewer than 38 ATP molecules for every glucose molecule that is oxidized through aerobic respiration?
5. What happens to electrons that accumulate at the end of the electron transport chain?
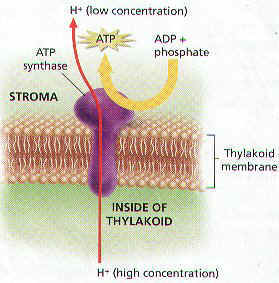
6. What role does chemiosmosis play in aerobic respiration?
7. What condition must exist in a cell for the cell to engage in fermentation?
8. How is the synthesis of ATP in the electron transport chain of mitochondria similar to the synthesis of ATP in chloroplasts?
9. The fourth step of glycolysis yields four ATP molecules, but the net yield is only two ATP molecules. Explain this discrepancy.
10. Under what conditions would cells in your body undergo lactic-acid fermentation?
11. What role does oxygen play in aerobic respiration? What molecule does oxygen become a part of as a result of aerobic respiration?
12. Where in the mitochondrion do protons accumulate, and what is the source of the protons?
 Across 2. a series of three mRNA nucleotides that codes for an amino acid 3. coded for by DNA and made of amino acids 7. process of assembling amino acids into polypeptides in the ribosomes 9. RNA that copies DNA in the nucleus 10. use to translate mRNA transcripts into proteins 11. UGA, UAA, and UAG codons 12. RNA that carries amino acids to be linked together to make proteins 15. site of transcription Down 1. both DNA and RNA are these types of compounds 2. where ribosomes are found 4. series of three bases on tRNA that code for an amino acid 5. base on RNA that replaces thymine 6. holes in the nuclear membrane where mRNA leaves to move to the ribosome 8. methionine codon (AUG) 13. RNA that makes up ribosomes along with proteins 14. site of protein synthesis
Across 2. a series of three mRNA nucleotides that codes for an amino acid 3. coded for by DNA and made of amino acids 7. process of assembling amino acids into polypeptides in the ribosomes 9. RNA that copies DNA in the nucleus 10. use to translate mRNA transcripts into proteins 11. UGA, UAA, and UAG codons 12. RNA that carries amino acids to be linked together to make proteins 15. site of transcription Down 1. both DNA and RNA are these types of compounds 2. where ribosomes are found 4. series of three bases on tRNA that code for an amino acid 5. base on RNA that replaces thymine 6. holes in the nuclear membrane where mRNA leaves to move to the ribosome 8. methionine codon (AUG) 13. RNA that makes up ribosomes along with proteins 14. site of protein synthesis