Autoimmune mechanisms underline many diseases, some organ-specific, others systemic in distribution.
Autoimmune disorders can overlap: an individual may have more than one organspecific disorder;or more than one systemic disease.
Genetic factors such as HLA type are important in autoimmune disease, and it is probable that each disease involves several factors.
Autoimmune mechanisms are pathogenic in experimental and spontaneous animal models associated with the development of autoimmunity.
Human autoantibodies can be directly pathogenic.
Immune complexes are often associated with systemic autoimmune disease.
Autoreactive B and T cells persist in normal subjects but in disease are selected by autoantigen in the production of autoimmune responses.
Microbial cross-reaching antigens and cytokine dysregulation can lead to autoimmunity.
Autoantibody tests are valuable for diagnosis and sometimes for prognosis.
Treatment of organ-specific diseases usually involves metabolic control.
Treatment of systemic diseases includes the use of anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive drugs.
Future treatment will probably focus on manipulation of the pivotal auto reactive T cells by antigens or peptides, by anti CD4 and possibly T cell vaccination.
THE ASSOCIATION OF AUTOIMMUNITY WITH DISEASE
The immune system has tremendous diversity and because the repertoire of specificities express by the B- and T-cell populations is generated randomly, it is bound to include many which are specific for self components. Thus the body must establish self-tolerance mechanisms, to distinguish between self and non-self determinants, so as to avoid auto reactivity (see Chapter 7). However, al mechanism has a risk of breakdown. The self recognition mechanisms are no exception, and a number of disease have been identified in which there is autoimmunity, due to copious production of autoantibodies and auto reactive T cells. One of the earliest examples in which the production of autoantibodies was associated with disease in a given organ is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Among the autoimmune diseases, thyroiditis has been particularly well-studied, and many of the aspects discussed in this chapter will draw upon our knowledge of it. It is a disease of the thyroid which is most common in middle-aged women and often lead to formation of a goiter and hypothyroidism.
The gland is infiltrated, sometimes to an extraordinary extent, with inflammatory lymphoid cells.
These are predominantly mononuclear phagocytes, lymphocytes and plasma cells, and secondary lymphoid follicles are common (Figure-1). In Hashimoto’s disease, the gland often shows regenerating thyroid follicles but this is not a feature of the thyroid in the related condition, primary myxoedema, in which comparable immunology features are seen and where the gland undergoes
almost complete destruction and shrinks. The serum of patients with Hashimoto’s disease usually contains antibodies to thyroglobulin. These antibodies are demonstrable by agglutination and by precipitin reactions when present in high titre. Most patients also have anti bodies directed against a
cytoplasmic or microsome antigen, also present on the apical surface of the follicular epithelial cells (Figure-2), and now known to be thyroid peroxidase, the enzyme which iodinates thyroglobulin.
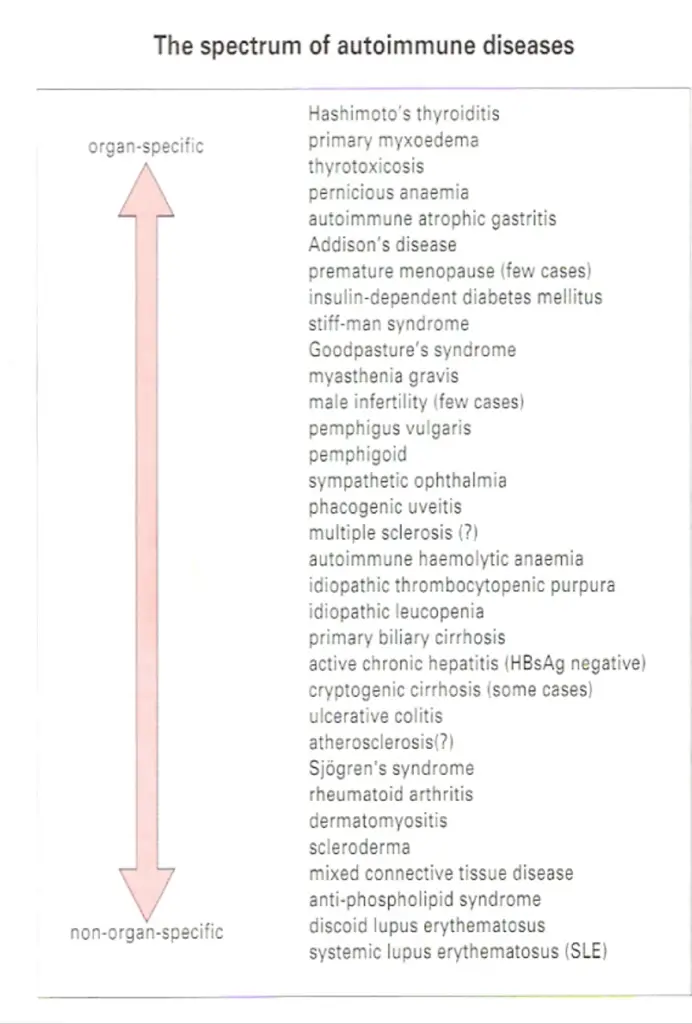
THE SPECTRUM OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
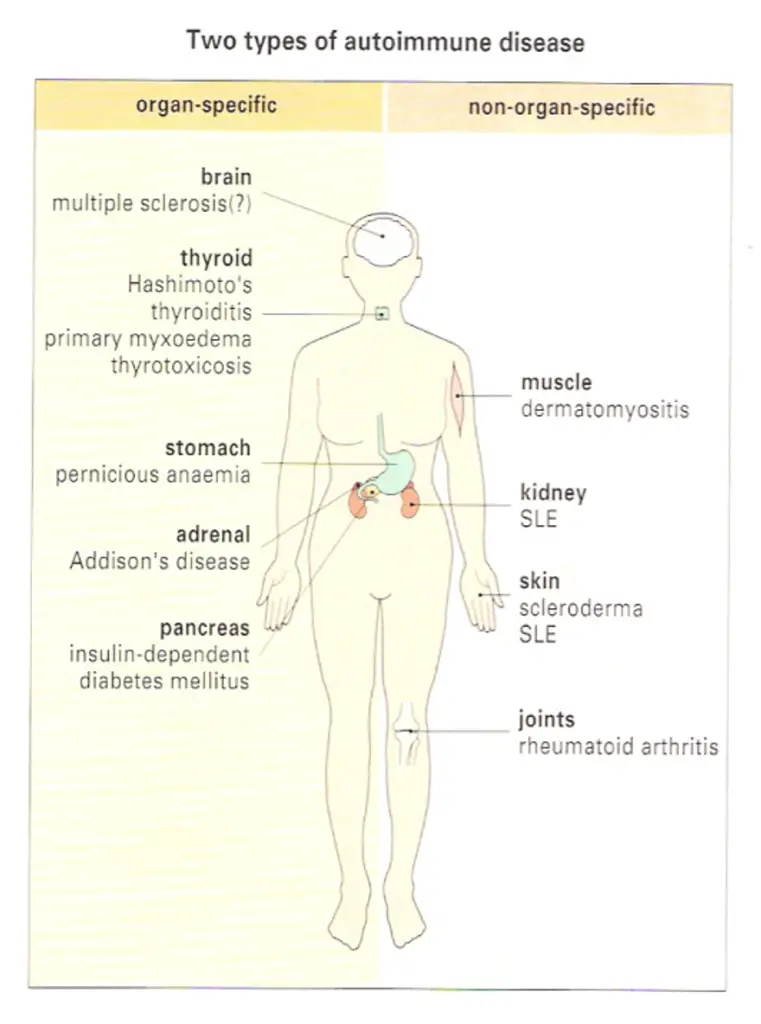
The antibodies associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and primary myxoedema react only with the thyroid, so the resulting lesion is highly localized. By contrast, the serum from patients with diseases such as systemic lupus crythematosus (SLE) reacts with many, if not all, of the tissues I the body. In SLE, one of the dominant antibodies is directed against the cell nucleus (Figure-2). These two diseases represent the extremes of the autoimmune spectrum (Figure-3). The common target organs in organ-specific disease include the thyroid, adrenals, stomach and pancreas. The non-organ-specific diseases, which include the rheumatological disorders, characteristically involve the skin, kidney, joints and muscle (Figure-4).
An individual may have more then one autoimmune disease
Interestingly, there are remarkable overlaps at each end of the spectrum. Thyroid antibodies occur with a high frequency in pernicious anaemia patients who have gastric autoimmunity, and these patients have a higher incidence of thyroid autoimmune disease than the normal population.
Similarly, patients with thyroid autoimmunity have a high incidence of stomach autoantibodies and, to a lesser extent, the clinical disease itself, namely pernicious anaemia. The cluster of hematological disorders at the other end of the spectrum also shows considerable overlap. Features of rheumatoid
arthritis, for example, are often associated with the clinical picture of SLE. In these diseases immune complexes are deposited systemically, particularly in the kidney, joints and skin, giving rise to widespread lesions. By contrast, overlap of diseases from the two ends of the spectrum is relatively
rare. The mechanisms of immunopathological damage vary depending on where the disease lies in the spectrum. Where the antigen is localized in a particular organ, Type II hypersensitivity and cell-mediated reactions are most important. In non-organ-specific autoimmunity, immune complex deposition leads to inflammation through a variety of mechanisms, including complement activation and phagocyte recruitment.
GENETIC FACTORS
Autoimmune disease can occur in families
There is an undoubted family incidence of autoimmunity. This is largely genetic rather than environmental, as many be seen from studies of identical and non-identical twins, and from the associated of thyroid autoantibodies with abnormalities of the Xchromosome. Within the families of patients with organ-specific autoimmunity, not only is there a general predisposition to develop organ-specific antibodies, it is also clear that other genetically controlled
factors tend to select the organ that is mainly affected. Thus, although relatives of Hashimoto patients and families of pernicious anaemia patients both have higher than normal incidence and titer of thyroid autoantibodies, the relatives of pernicious anaemia patients have a far higher frequency of gastric autoantibodies, indicating that there are genetic factors which differentially
select the stomach as the target within these families.
Certain HLA Haplotypes Predispose To Autoimmunity
Further evidence for the operation of genetic factors in autoimmune disease comes from their tendency to be associated with particular HLA specificities (Figure-5). Rheumatoid arthritis shows no associations with the HLA-A and-B loci haplotypes, but is associated with a nucleotide sequence (encoding amino
acids 70-74 in the DRβ chain) that is common to DR1 and major subtypes of DR4.
This sequence is also present in the dnaJ heat-shock proteins of various bacilli and EBV gp 110 proteins, presenting an interesting possibility for the induction of autoimmunity by a microbial cross-reacting epitope (see below). The plot gets even deeper, though, with the realization that HLA-DR molecules bearing this sequence can bind to another bacterial heat shock protein, dna K, and to the human analogue, namely hsp73, which targets selected proteins to lysosomes for antigen processing. The haplotype B8, DR3 is particularly common in the organ specific diseases, although Hashimoto’s thyroiditis tends to be associated more with DR5. It is notable that for insulin-dependent (type 1) diabetics mellitus, DQ2/8 heterozygotes have a greatly increased risk of
developing the disease (Figure-5). Although HLA risk factors tend to dominate-wide searches for mapping the genetic intervals containing genes for predisposition to disease by linkage to micro satellite markers (polymorphic variable numbers of tandem repeats, VNTR) reveal a plethora of genes affecting loss of tolerance, sustained inflammatory responses and end-organ targeting.
Pathogenesis
Autoimmune processes are often pathogenic. When autoantibodies are fond in association with a particular disease there are three possible inferences:
• The autoimmunity is responsible for producing the lesions of the disease.
• There is a disease process which, through the production of tissue damage, leads to the development of autoantibodies.
• There is a factor which produces both the lesions and the autoimmunity. Autoantibodies secondary to a lesion (the second possibility) are sometimes found. For example, cardiac autoantibodies may develop after myocardial infarction. However, sustained production of autoantibodies rarely follows the release of autoantigens by simple trauma. In most diseases associated with autoimmunity, the evidence supports the first possibility, that the autoimmune
process produces the lesions.
The pathogenic role of autoimmunity can be demonstrated in experimental models
Examples of induced autoimmunity
The most direct test of whether autoimmunity is responsible for the lesions of disease is to induced autoimmunity deliberately in an experimental animal and see if this leads to the production of the lesions. Autoimmunity can be induced in experimental animals by injecting auto antigen (self antigen) together with complete Freund’s adjuvant, and this does indeed produce organ-specific
disease in certain organs. For example, thyroglobulin injection can induce an inflammatory disease of the thyroid while myelin basic protein can cause encephalomyelitis. In the case of thyroglobulin-injected animals, not only are thyroid autoantibodies produced, but the gland becomes infiltrated with mononuclear cells and the acinar architecture crumbles, closely resembling the histology of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. The ability to induce experimental autoimmune disease depends on the strain of animal used.
For example, it is found that the susceptibility of rats and mice to myelin basic protein-induced encephalomyelitis depends on a small number of gene loci, of which the most important are the MHC class II genes. The disease can be induced in susceptible strains by injecting T cells belong to the CD4/TH1 subset and it has been found that induction of disease can be prevented by treating
the recipients with antibody to CD4 just before the expected time of disease onset, blocking the interaction of the TH cells’ CD4 with the class II MHC of antigen-presenting target cells. The results indicate the importance of class II restricted auto reactive TH cells I the development of these conditions, and emphasize the prominent role of the MHC.
Examples of spontaneous autoimmunity
It has proved possible to breed strains to animals which are genetically programmed to develop autoimmune diseases closely resembling their human counterparts. One well established example is the Obese strain (OS) chicken (Figure-6) which parallels human autoimmune thyroid disease in terms
of the lesion in the gland, the production of antibodies to different components in the thyroid, and the overlap with gastric autoimmunity. So it is of interest that when the immunological status of these animals is altered, quite dramatic effects on the outcome of the disease are seen.
For example, removal of the thymus at birth appears to exacerbate the thyroiditis, suggesting that the thymus exerts a controlling effect on the disease, but if the entire T-cell population is abrogated by combining thymectomy with massive injections of anti-chick T-cell serum, both autoantibody production and the attack on thyroid are completely inhibited. Thus, T cells play a variety of pivotal roles as mediators and regulators of this disease. The non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse provides an excellent model for human insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM; type 1 diabetes) where the
insulin producing β cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans are under attack from a chronic leukocytic infiltrate of T cells and macrophages (Figure-7). The role of the T cells in mediating this attack is evident from the amelioration and prevention of disease by treatment of the mice with a non-depending anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody, which in the presence of the pancreatic auto-antigens, insulin and glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) induces specific T cell anergy.
The dependence of yet another spontaneous model, the F1 hybrid of New Zealand Black and White strains (NZB x W/F1), on the operation of immunological processes is aptly revealed by the suppression of the murine SLE which characterizes this strain, by treatment with anti-CD4 (Figure-8).
Human autoantibodies can be directly pathogenic
When investigating human autoimmunity directly, rather than using animal models, it is of course more difficult to carry out experiments. Nevertheless, there is much evidence to suggest that autoantibodies may be important in pathogenesis, and we will discuss the major examples here.
Thyroid autoimmune disease – A number of disease have been recognized in which autoantibodies to hormone receptors may actually mimic the function of the normal hormone concerned and produce disease. Graves’ disease (thyrotoxicosis) was the first disorder in which such anti-receptor antibodies were clearly recognized. The phenomenon of neonatal thyrotoxicosis provides us with a natural ‘passive transfer’ study, because the IgG antibodies from the thyrotoxic mother cross the placenta and react directly with thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor o the neonatal thyroid.
Many babies born to thyrotoxic mothers and showing thyroid hyperactivity have been reported, but the problem spontaneously resolves as the antibodies derived from the mother are catabolized in the baby over several weeks. Whereas autoantibodies to the TSH receptor may stimulate cell division and/or increase the production of thyroid hormones, others can bring about the opposite effect by inhibiting these functions, a phenomenon frequently observed in the receptor responses to ligands which act as agonists or antagonists. Different combinations of the various manifestations of
thyroid autoimmune disease, chronic inflammatory cell destruction and stimulation or inhibition of growth and thyroid hormone synthesis, can give rise to a wide spectrum of clinical thyroid dysfunction (Figure-9).
Myasthenia gravis – A parallel with neonatal hyperthyroidism has been observed with mothers suffering from myasthenia gravis, where antibodies to acetylcholine receptors cross the placenta into the fetus and may cause transient muscle weakness in the newborn baby.
Other receptor diseases – Somewhat rarely, autoantibodies to insulin receptors and to βadrenergic receptors can be found, the latter associated with bronchial asthma. Neuromuscular defects can be elicited in mice injected with serum from patients with the Lambert – Eaton syndrome containing antibodies to presynaptic calcium channels, while sodium channel autoantibodies have been identified in the Guillain – Barre syndrome.
Male infertility – Yet another example of autoimmune disease is seen in rate cases of male infertility were antibodies to spermatozoa lead to clumping of spermatozoa, either by their heads or by their tails, in the semen.
Pernicious anaemia – In this disease an autoantibody interferes with the normal uptake of vitamin B12.Vitamine B12 is not absorbed directly, but must first associated with a protein called intrinsic factor; the vitamin-protein complex is then transported across the intestinal mucosa. Early passive transfer studies demonstrated that serum from a patient with pernicious anaemia, if fed to a healthy individual together with intrinsic factor – B12 complex, inhibited uptake of the vitamin.
Subsequently, the factor in the serum which blocked vitamin uptake was identified as antibody against intrinsic factor. It is now known that plasma cells in the gastric mucosa of patients with pernicious anaemia secrete this antibody into the lumen of the stomach (Figure-10).
Goodpasture’s syndrome – In goodpasture’s syndrome, antibodies to the glomerular capillary basement membrane bind to the kidney in vivo (Figure-3). To demonstrate that the antibodies can have a pathological effect, a passive transfer experiment was performed. The antibodies were eluted from the kidney of a patient who had died with this disease, and injected into primates whose kidney antigens were sufficiently similar for the injected antibodies to localize on the glomerular basement membrane. The injected monkeys subsequently died with glomerulonephritis.
Blood and vascular disorders – Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia and idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura result from the synthesis of autoantibodies to red cells and platelets, respectively. The
primary antiphospholipid syndrome characterized by recurrent thromboembolic phenomena and feta loss is triggered by the reaction of autoantibodies with a complex of β2-glycoprotein turns up again as an abundant component of atherosclerotic plaques and there is increasing attention to the idea that autoimmunity may initiate or exacerbate the process of lipid deposition and plaque formation in this disease, the two lead candidate antigens being heat-shock protein 60 and the low- density lipoprotein, apoprotein B. The necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis which characterizes
Wegener’s granulomatosis is associated with antibodies to neutrophil cytoplasmic proteinase III (cANCA) but their role in pathogenesis of the vaculitis is ill defined.
Immune Complexes appear to be pathogenic in systemic autoimmunity
In the case of SLE, it can be shown that complement-fixing complexes of antibody with DNA and other nucleosome components such as histones are deposited in the kidney (Figure-3), skin, joints and choroid plexus of patients, and must be presumed to produce Type III hypersensitivity reactions.
Cationic anti-DNA antibodies and histones facilitate the binding to heparin sulphate in the connective tissue structures. Individuals with genetic deficiency of the early classical pathway complement components clear circulating immune complexes very poorly and are unduly susceptible to the development of SLE. Turing to the experimental models, we have already mentioned the (NZB x W) F1 which spontaneously develops murine SLE associated with immune-complex glomerulonephritis and anti-DNA autoantibodies as major features. The fact that measures which suppress the immune response in these animals (e.g. treatment with azathioprine or anit-CD4) also suppress the disease and prolong survival, adds to the evidence for autoimmune reactions causing such disease (Figure-8).
The erosions of cartilage and bone in rheumatoid arthritis are mediated by macrophages and fibroblasts which become stimulated by cytokines from activated T cells and immune complexes generated by a vigorous immunological reaction within the synovial tissue. The complexes can arise
through the self-association of IgG rheumatoid factors specific for the Fcy domains, a process facilitated by the striking deficiency of terminal galactose on the biantennary N-linked Fc iligosaccharides (Figure-11). This agalacto glycoform of IgG in complexes can exacerbate inflammatory reactions through reaction with mannosebinding lectin and production of TNE.
Evidence for directly pathogenic T cells in human autoimmune disease is hard to get
Adoptive transfer studies have shown that TH1 cells are responsible for directly initiating the lesions in experimental models of organ-specific autoimmunity. In the human, the production of high affinity, somatically mutated IgG autoantibodies characteristic of Tdependent responses, the isolation of thyroid-specific T-cell clones from the glands of Graves’ disease patients, the beneficial effect of cyclosporine in pre-diabetic individuals and the close association with certain HLA haplotypes, make it abundantly clear that T cells are utterly pivotal for the development of autoimmune disease. However, it is difficult to identify a role for the T cell as a pathogenic agent as
distinct from a T-helper function in the organ-specific disorders. Indirect evidence from circumstances showing that antibodies themselves do not cause disease, such as in babies born to mothers with insulin-dependent diabetes (IDDM), may be indicative.
Autoimmunity is antigen driven
Given that auto-reactive B cells exist, the question remains whether they are stimulated to proliferate and produce autoantibodies by interaction with auto-antigens or by some other means, such as non-specific polyclonal activators or idiotypic interactions (Figure-14). Evidence that B cells are selected by antigen comes from the existence of high affinity autoantibodies which arise through
somatic mutation, a process which requires both T cells and autoantigen.
Additionally, autoantibodies to epitope clusters occur on the same auto-antigenic molecule. Apart from the presence of auto-antigen itself, it is very difficult to envisage a mechanism that could account for the co-existence of antibody responses to different epitopes on the same molecule. A similar argument applies to the induction, in a single individual, of autoantibodies to organcelles (e.g. nucleosomes and spliceosomes which appear as belbs on the surface of apoptotic cells) or antigens linked within the same organ (e.g. thyroglobulin and thyroid peroxidase).
The most direct evidence for autoimmunity being antigen driven comes from studies of the Obese strain chicken which, as described earlier, spontaneously develops thyroid autoimmunity. If the thyroid gland (the source of antigen) is removed at birth, the chickens mature without developing
thyroid autoantibodies (Figure-13). Furthermore, once thyroid autoimmunity has developed, later removal of the thyroid leads to a gross decline of thyroid autoantibodies, usually to undetectable levels. Comparable experiments have been carried out in the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse which models human autoimmune diabetes; chemical destruction of the β cells leads to decline in
pancreatic autoantibodies. DNase treatment of lupus mice ameliorates the disease, presumably by destroying potentially pathogenic immune complexes.
In organ-specific disorders, there is ample evidence for T cells responding to antigens present in the organs under attack. But in non-organ-specific autoimmunity, identification of the antigens recognized by T cells is often inadequate. True, histone-specific T cells are generated in SLE patients
and histone could pay a ‘piggy back’ role in the formation of anti-DNA antibodies by substituting for natural antibody in the mechanism outlined in Figure-14. Another possibility is that the T cells do not see conventional peptide antigen (possibly true of anit-DNA responses) but instead recognize an
antibody’s idiotype (an antigenic determinant on the V region of antibody). In this view SLE, for example, might sometimes be initiated as an ‘idiotype disease’, like the model presented in Figure-14 In this scheme, autoantibodies are produced normally at low levels by B cells using germ-line genes. If these then form complexes with the autoantigen, the complexes can be taken up by APCs (including B cells) and components of the complex, including the antibody idiotype, presented to T cells. Idiotype-specific T cells would then help the autoantibody-producing B cells. Evidence for the induction of anti-DNA and glomerulonephritis by immunization of mice with the idiotype of germ-line ‘natural’ antiDNA autoantibody lends credence to this hypothesis.
Controls on the development of autoimmunity can be bypassed in a number of ways
Molecular mimicry by cross-reactive microbial antigens can stimulate autoreactive B and T cells
Normally, naïve autoreactive T cells recognizing cryptic self epitopes are not switched on because the antigen is only presented at low concentrations on ‘professional’ APCs or it may bepresented on ‘non-professional’ APCs such as pancreatic β-islet cells or thyroid epithelial cells, which lack B7 or other co-stimulator molecules. However, infection with a microbe bearing antigens that cross-react with the cryptic self epitopes (i.e. have shared epitopes) will load the professional APCs with levels of processed peptides that are sufficient to activate the naïve autoreactive T cells. Once primed, these T cells are able to recognize and react with the self epitope on the non-professional APCs since they no longer require a co-stimulatory signal and have a higher avidity for the target, due to upregulationof accessory adhesion molecules (Figure-15).
Cross reactive antigens which share B cell epitopes with self molecules can also break tolerance but by a different mechanism. Many autoreactive B cells cannot be activated because the CD4+ helper T cells which they need are unresponsive either because these helper T cells are tolerized at lower concentration of autoantigens than the B cells or because they only recognize cryptic epitopes. However, these ‘helpless’ B cells can be stimulated if the cross-reaching antigen bears a ‘foreign’ carrier epitope to which the T cells have not been tolerized (Figure-16). The autoimmune process may persist after clearance of the foreign antigen if the activated B cells now focus the autoantigen on their surface receptors and present it to normally resting autoreactive T cell which will then proliferate and act as helpers for fresh B-cell stimulation.
A disease in which such molecular mimicry operates is rheumatic fever, in which autoantibodies to heart valve antigen can be detected. These develop in a small proportion of individuals several weeks after a streptococcal infection of the throat. Carbohydrate antigens on the streptococci cross-react with an antigen on heart valves, so the infection may bypass T-cell self tolerance to heart valve antigens. Shared B-cell epitopes between Yersinia enterolytica and the extracellular domain of the TSH receptor have recently been described. There may also be cross reactivity between HLA-B27 and certain strains of Klebsiella in connection with ankylosing spondylitis, and crossreactivity between bacterial heat-shock proteins and DR4 in relationship to rheumatoid arthritis.
In this connection, it has been suggested that because processed MHC molecules may represent a major fraction of the peptide emitopes presented to differentiating T cells within the thymus, a significant proportion of positively selected cell which escape negative selection and enter the periphery will be specific for weakly binding cryptic MHC epitopes. One might therefore expect autoimmune responses to arise not infrequently through activation of these cells by molecular mimicry.
In some cases foreign antigen can directly stimulate auto-reactive cells
Another mechanism to bypass the tolerant autoreactive TH cell is where antigen or another stimulator directly triggers the autoreactive effector cells. For example, lipopolysaccharide or Epstein-Barr virus causes direct B-cell stimulation and some of the clones of activated cells will produce autoantibodies, although in the absence of T-cell help these are normally of low titer and affinity. However, it is conceivable that an activated B cell might pick up and process its cognate autoantigen and present it to a naïve autoreactive T cell.
Cytokine dysregulation, inappropriate MHC expression and failure of suppression may induce autoimmunity
It appears that dysregulation of the cytokine network can also lead to activation of autoreactive T cells. One experimental demonstration of this is the introduction of a transgene for interferon-γ (IFNγ) into pancreatic β-islet cells. If the transgene for IFNγ is fully expressed in the cells, MHC class II genes are upregulated and autoimmune destruction of the islet cell results (Figure-17). This is not simply a result of a nonspecific chaotic IFNγ-induced local inflammatory milieu since normal islets grafted at a separate site are rejected, implying clearly that T-cell autoreactivity to the pancreas has been established.
The surface expression of MHC class II in itself is not sufficient to activate the naïve autoreactive T cells but it may be necessary to allow a cell to act as a target for the primed autoreactive TH cells, and it was therefore most exciting when cells taken from the glands of patients with Graves’ disease were found to be actively synthesizing class II MHC molecules (Figure-18) and so were able to be recognized by CD4+ T cells. In this context it is interesting that isolated cells from several animal strains that are susceptible to autoimmunity are also more readily induced by IFNγ to express MHC class II than are cells from non-susceptible strains.
The argument that imbalanced cytokine production may also contribute to autoimmunity receives further support from the unexpected finding that tumour necrosis factor (introduced by means of a TNF transgene) ameliorates autoimmune disease in NZB x NZW hybrid mice.
Aside from the normal ‘ignorance’ of cryptic self-epitopes, other factors which normally restrain potentially autoreactive cells may include regulatory T cells, hormones (e.g. steroids), cytokines (e.g. TGFβ) and products of macrophages (Figure-19). Deficiencies in any of them may increase susceptibility to autoimmunity. The feedback loop on Thelpersand macrophages through the pituitary – adrental axis is particularly interesting, as defects at different stages in the loop turn up in a variety of autoimmune disorders Figure-20). For example, patients with rheumatoid arthritis have low circulating corticosteroid levels compared with controls, and after surgery, although they produce copious amounts of IL-1
and IL-6, a defect in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus prevents the expected increase in ACTH and adrenal steroid output. A subset of CD4 regulatory cell present in young healthy mice of the NOD strain can prevent the transfer of disease by spleen cells of diabetic animals to NOD mice congenic for the severe combined immunodeficiency trait; this regulatory subset is lost in older mice.
Pre-existing defects in the target organ may increase susceptibility to autoimmunity
We have already alluded to the undue sensitivity of target cells to upregulation of MHC class II by IFNγ in animals susceptible to certain autoimmune disease: Other evidence also favours the view that there may be a pre-existing defect in the target organ. In the Obese strain chicken model of spontaneous thyroid autoimmunity, not only is there a low threshold of IFNγ induction of MHC class II expressin by thyrocytes but it has also been shown that, when endogenous TSH is suppressed by thyroxine treatment, the uptake of iodine into the thyroid glands is far higher in the Obese strain than in a variety of normal strains. Furthermore, this is not due to any stimulating animals show even higher uptakes of iodine (Figure-21). Interestingly, the Cornell strain (from which the Obese strain was derived by breeding) shows even higher uptakes of iodine, yet these animals do not develop spontaneous thyroiditis. This could be indicative of a type of abnormal thyroid behavior which in itself is insufficient to induce autoimmune disease but does contribute to susceptibility in the Obese strain. Other situations in which the production of autoantigen is affected are diabetes, in which one of the genetic risk factors is associated with a microsatellite marker lying within a transcription factor controlling the rate of insulin production, and rheumatoid arthritis, in which the agalacto IgG glycoform is abnormally abundant. The intriguing observations that immunization atherosclerotic lesions at classical predilection sites object to major haemodynamic stress and that patients with atherosclerosis produce antibodies to human hsp60 which react with heat or IFNα-stressed endothelial cells, hints strongly at an autoimmune contribution to the pathology of the disease. Particularly relevant to the present discussion is the finding of upregulated hasp60 expression at such critical sites even in a 5-month-old child (Figure22). Again, one must re-emphasize the considerable importance of multiple factors I the establishment of prolonged autoimmunity.
DIAGONOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF AUTOANTIBODIES
Wherever the relationship of autoantibodies to the disease process, they frequently provide valuable markers for diagnostic purposes. A particularly good example is the test for mitochondrial antibodies, used in diagnosing primary biliary cirrhosis (Figure-23). Exploratory laparotomy was previously needed to obtain this diagnosis, and was often hazardous because of the age and condition of the patients concerned. Autoantibodies often have predictive value. For instance, individuals testing positively for antibodies to both insulin and glutamic acid decarboxylase have a high risk of developing insulin-dependent diabetes.
TREATMENT
Often, in organ-specific autoimmune disorders, the symptoms can be conrolled by administration of thyroxine, and thyrotoxicosis by antithyroid drugs. In pernicious anaemia,
metabolic correction is achieved by injection of vitamin B12, and in myasthenia gravis by administration of cholinesterase inhibitors. If the target organ is not completely destroyed, it may be possible to protect the surviving cells by transfection with FasL or TGFβ genes. Where function is completely lost and cannot be substituted by hormones, as many occur in lupus nephritis or chronic rheumatoid arthritis, tissue grafts or mechanical substitutes may be appropriate. In the case of tissue grafts, protection from the immunological processes which necessitated the transplant may be required.
Conventional immunosuppressive therapy with antimitotic drugs at high doses can be used to dam down the immune response but, because of the dangers involved, tends to be used only in life-threatening disorders such as SLE and dermatomyositis. The potential of cyclosporine and related drugs such as rapamycin has yet to be fully realized, but quite dramatic results have been reported in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Anitinflammatory drugs are, of course, prescribed for rheumatoid diseases with the introduction of selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors representing a welcome development. Encouraging results are being obtained by treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients with low steroid doses at an early stage to correct the apparently defective production of these corticosteroids by the adrenal feedback loop, and for those with more established disease, attention is now focused on the striking remissions achieved by synergistic treatment with anti-TNFα monoclonals plus methotrexate.
As we understand more about the precise defects, and learn how to manipulate the immunological status of the patient, some less well-established approaches may become practicable (Figure-24). Several centres are trying out autologous stem-cell transplantation following haemato-immunoablation with cytotoxic drugs in severe cases of SLE, scleroderma and rheumatoid arthritis. Draconian reduction in the T cells in multiple sclerosis by Campath-1H (anti-CD52) and of the B-cell population with antiCD20 in rheumatoid arthritis are both under scrutiny. Treatment with Campath-1H followed by a non-depleting anti-CD4 has produced excellent remissions in patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis who were refractory to normal treatment. In an attempt to establish antigenspecific suppression, considerable clinical improvement has been achieved in exacerbating remitting multiple sclerosis by repeated injection of Cop 1, a random copolymer of alanine, glutamic acid, lysine and tyrosine meant to simulate the postulated ‘guilty’ autoantigen, myelin basic protection. Some experimental autoimmune disease have been treated successfully by feeding antigen to induce oral tolerance, by the inhalation of autoantigenic peptides and their analogues (Figure-25), and by ‘vaccination’ with peptides from heat-shock protein 70 or the antigen-specific receptor or autoreactive T cells. This suggests that stimulating normally suppressive functions, including the idiotype network, could be promising.
CRITICAL THINKING: Autoimmunity and autoimmune disease
Miss Jacob, a 30-year-old Caribbean lady, was seen in a rheumatology clinic with stiff painful joints in her hands, which were worse first thing in the morning. Other symptoms included fatigue, a low-grade fever, a weight loss of 2 kg, and some mild chest pain. Miss Jacob had recently returned to the UK from a holiday in Jamaica and was also noted to be taking the combined oral contraceptive pill. Past medical history of note was a mild autoimmune haemolytic anaemia 2 years previously. On examination Miss Jacob had a non-specific maculopapular rash on her face and chest and patchy alopecia (hair loss) over her scalp. Her mouth was tender and examination revealed an ulcer on the soft palate. She had moderately swollen and tender proximal interphalangeal joints. Her other joints were unaffected, but she had generalized muscle aches. The results of investigations are shown in Figure-26.