| DNA & Protein Synthesis |  |
Section 10-1 DNA
1. What does DNA stand for?
2. What is DNA’s primary function?
3. What is the function of proteins?
4. What are the repeating subunits called that make up DNA?
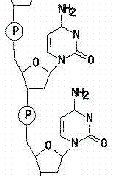
5. Name the 3 parts of a DNA nucleotide.
6. Sketch and label a DNA nucleotide.
7. Name the 4 nitrogen bases on DNA.
8. What is the difference between a purine & a pyrimidine?
9. Name 2 purines.
10. Name 2 pyrimidines.
11.Who is responsible for determining the structure of the DNA molecule & in what year was this done?
12. The model of DNA is known as a ____________________________ because it is composed of two ___________________ chains wrapped around each other.
13. What makes up the sides of a DNA molecule?
14. What makes up the “steps” of a DNA molecule?
15. How did Rosalind Franklin contribute to determining the structure of DNA?
16. What type of bonds holds the DNA bases together? Are they strong or weak bonds?
17. What makes up the “backbone” of the DNA molecule?
18. On DNA, a ____________________ base will always pair with a __________________ base.
19. What is the most common form of DNA found in organisms?
20. How many base pairs are in a full turn or twist of a DNA molecule?
21. Name the complementary base pairs on DNA.
22. How many hydrogen bonds link cytosine & guanine? adenine & thymine?
23. How does the nucleotide sequence in one chain of DNA compare with the other chain of DNA?
24. Why must DNA be able to make copies of itself?
25. Define DNA replication.
26. What is the first step that must occur in DNA replication?
27. What acts as the template in DNA replication?
28. What is a replication fork?
29. What enzymes help separate the 2 strands of nucleotides on DNA? What bonds do they break?
30. What is the function of DNA polymerases?
31. ____________________ are joined to replicating strands of DNA by ________________ bonds.
32. If the sequence of nucleotides on the original DNA strand was A – G – G – C – T – A, what would be the nucleotide sequence on the complementary strand of DNA?
33. Does replication of DNA begin at one end and proceed to the other? Explain.
34. Why does DNA replication take place at many places on the molecule simultaneously?
35. When replication is complete, how do the 2 new DNA molecules compare to each other & the original DNA molecule?
36. Is DNA replicated (copied) before or after cell division?
37. Sketch & label DNA replication. (Figure 10-5, page 188)
38. What is the error rate in DNA replication? What helps lower this error rate to 1 in 1 billion nucleotides?
39. What is a mutation?
40. Name several things that can cause DNA mutations.
Section 10-2 RNA
41. What sugar is found on DNA?
42. What base is missing on RNA, & what other base replaces it?
43. Uracil will pair with what other on DNA?
44. Is RNA double or single stranded?
45. Name the 3 types of RNA and tell the shape of each.
46. Which type of RNA copies DNA’s instructions in the nucleus?
47. Which type of RNA is most abundant?
48. What does tRNA transport?
49. What 2 things make up ribosomes?
50. Define transcription.
51. In what part of a cell are proteins made?
52. What is RNA polymerase & tell its function.
53. What are promoters?
54. Where does RNA polymerase bind to the DNA it is transcribing?
55.What makes the beginning of a new gene on DNA in eukaryotes?
56. What do promoters mark the beginning of on prokaryotic DNA?
57. When a promoter binds to DNA, What happens to the double helix?
58. Are both strands of DNA copied during transcription?
59. As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template strand, what is being added?
60. What bases pair with each other during transcription?
61. What is the termination signal?
62. What happens when RNA polymerase reaches the termination signal?
63. What are the products of transcription called?
64. Transcripts are actually ____________________________ molecules.
65. In transcription, ________________________’s instructions for making a protein
are copied by _______________________.
66. Which RNA molecules are involved in the synthesis (making) of a protein?
67. What happens to the newly made mRNA molecule following transcription in the nucleus?
Section 10-3 Protein Synthesis
68. What makes up proteins, what are the subunits called, & what bonds them together?
69. How many different kinds of amino acids make up proteins?
70. What determines how protein polypeptides fold into 3-dimensional structures?
71. Why does a protein need a 3-dimensional structure?
72. What is the genetic code & why is it important?
73. What is a codon & what does each codon code for?
74. How many codons exist?
75. Name the amino acid coded for by each of these codons:
a. UUA
b. AUU
c. UGU
d. AAA
e. GAG
f. UAA
76. What codon starts protein synthesis?
77. What codons stop protein synthesis?
78. Proteins are synthesized (made) at what organelle in the cytosol?
79. Sketch and label a tRNA molecule & tell its function.
80. Define translation & tell how it starts.
81. Where are amino acids found in a cell & how are they transported?
82. What is an anticodon & where is it found on tRNA?
83. What codon on mRNA would bind with these anticodons: (use table 10-1, page 194)
a. AAA
b. GGA
c. UAC
d. CGU
84. What are ribosomes made of and in what 2 places can they be found in a cell?
85. What is the difference between proteins made by free ribosomes & those made by attached, membrane proteins on the ER?
86. How many binding sites are found on the ribosomes and what does each site hold?
87. To start making a protein or _________________________________, a ribosome attaches to the ______________________________ codon on the __________________ transcript.
88. The start codon, AUG, pairs with what anticodon on a tRNA molecule?
89. What amino acid does the start codon always carry?
90. What type of bonds are the ones that attach amino acids to each other in a growing polypeptide?
91. __________________________ are linked to make proteins as a ______________________ moves along the mRNA transcript.
92. What ends translation?
93. Can more than one ribosome at a time translate an mRNA transcript? Explain.
94. What determines the primary structure of a protein?
95. What would the translation of these mRNA transcripts produce?
a. UAA CAA GGA GCA UCC
b. UGA CCC GAU UUC AGC