PreAP Biology Project Due Dates

| Project | Due Date |
PreAP Biology Project Due Dates

| Project | Due Date |
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
1. Cells that support the non-growing parts of plants are called ____________________.
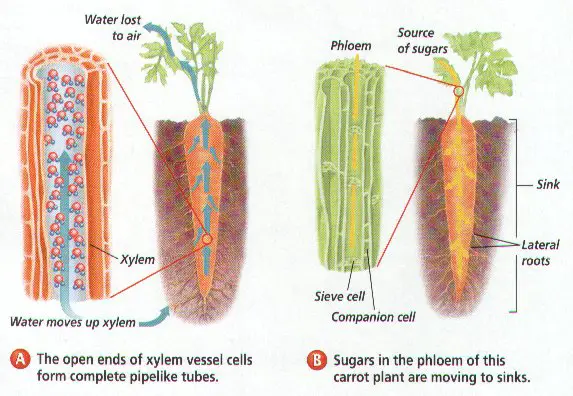
2. Sugars are transported in vascular plants through what tissue?
3. The tissue in a vascular plant that is used to transport water and minerals is __________.
4. Which plant cells are the most abundant and least structurally specialized?
5. Long, narrow cells of xylem with thin separations between them are known as _______.
6. Short, wide cells of xylem with NO end walls function in water transport when the cells are __________.
7. Cells of phloem that help the sieve tube elements to function are called _________________.
8. Growth that makes a plant stem thicker is known as ____________________ ____________.
9. In the meristem regions of plants you would expect to find _____________________ cells.
10. Collenchyma cells would help support which parts of a celery plant?
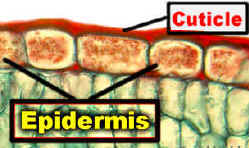
11. The epidermis on the stems and leaves of young plants prevents ______________________.
12. The vascular cylinder of a root is surrounded by the __________________________.
13. A plant absorbs water and minerals through _____________________.
14. Which type of plant cells function in metabolic activities such as photosynthesis, storage, and healing?
15. Grasses usually have which type of roots?
16. In stems, vascular tissue is arranged to form ________________________.
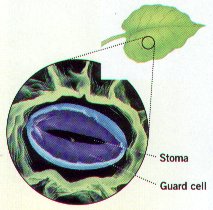
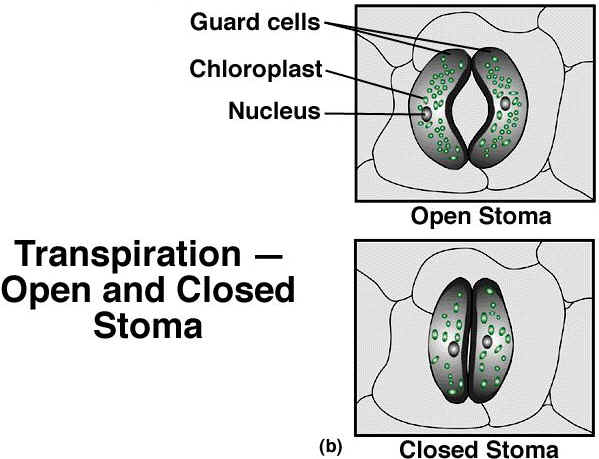
17. What are the pores in the epidermis of leaves that control water evaporation called?
18.Primary growth in roots results in _________________________ of roots, and secondary growth results in _________________________ of roots.
19. What is the process of the evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant called?
20. The movement of sugars in a plant can be explained by the __________-
_____________ _____________.
21. What causes water molecules to stick together and pull each other up a plant stem?
22. Sugars made in photosynthesis in transported by being pumped into the ___________________________ _______________________________.
23. The function of the endodermis in roots is to _____________________ movement of substances into the ________________________ ___________________ of the root.
24. _______________________________ tissue forms the skin of a plant.
25. ______________________________ tissue consists of everything that is Not dermal or vascular tissue.
26. The growing regions of plants are called ________________________________________.
27. Meristematic tissue is the only type of plant tissue that produces new cells by _______________.
28. The elongation of stems and roots is called _____________ _______________.
29. Most seed plants have Three basic organs, _________________, ___________________ and
_______________________________.
30. Lateral roots form from the _______________________ inside the root, while lateral stems form from _____________________________ on the surface of stems.
31. Plant cells that are even, thick-walled, rigid cells _____________________________.
32. The name of the meristem between xylem and phloem _______________________.
33. The roots that branch off a primary root ________________________ _________________.
34. Plant cells that are irregular, thick-walled cells ______________________________.
35. A root system with an enlarged primary root _________________________.
36. Type of meristems found only in monocots _________________________.
37. Type of root system with many branch roots _______________________.
38. Type of plants cells that are thin-walled cells that can be cube-shaped or elongated _______________.
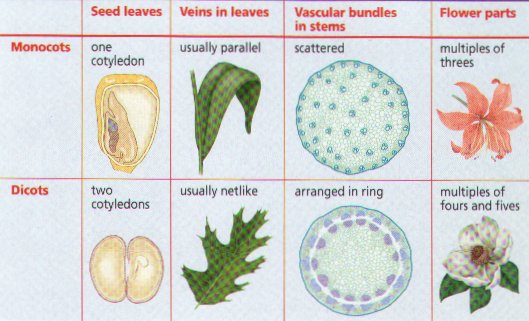
39. In Dicots primary growth occurs in _______________________ ________________________ and in monocots it occurs in _______________________ ______________________ and may also occur in _________________________ _________________________.
40. Primary growth results in the ________________________ of plant structures, and secondary growth results in the _____________________ of plant structures.
41. Monocots stems lack ____________________ ____________________ and therefore cannot produce _________________________ growth.
42. Annual rings in woody plants form as a result of the production of _____________________ ___________________, which contain cells of different sizes that were produced during different times of the growing season.
43. Water is transported from the roots to the leaves of a plant by the process of ___________.
Short Answer:
Answer the questions below as completely and as thoroughly as possible. Answer the question in essay
form (not outline form), using complete sentences. You may use diagrams to supplement your answers.
What are the TWO different types of vascular tissue in plants? Briefly describe each kind.
2. How are carbohydrates transported throughout a plant? (Explain the pressure-flow hypothesis).
3. Describe tracheids and explain their function.
4. What are the lateral meristems of plants, and what is their function?
5. What is the difference between primary growth and secondary growth?
6. Explain the main functions of stems, roots and leaves.
7. What adaptations of root maximize water and mineral absorption?
8. Identify the structures that a water molecule would move through on its way from the soil into the xylem of a plant root.
9. What is the relationship between stomata and guard cells? Describe how they function and Describe their role in the activities conducted by leaves.
10. What is transpiration? How is it related to the movement of water in plants?
11. What is the relationship between the Source and the Sink in the transport of sugars?
12. What are the Four types of tissue found in plants?
13. What are the Three basic types of plant cells? What are the functions of each?
14. Explain the cohesion-tension theory.
15. List five differences and five similarities between the structure of roots and the structure of stems.
   |
PreAP Biology Chapter Reviews |    |
| All Materials © Cmassengale |
| Plant Origin & Classification All Materials © Cmassengale |
 |
Overview of Plants:
Terrestrial Adaptations:
Copyright Holt, Rinehart, & Winston
Copyright Holt, Rinehart, & Winston
copyright McGraw-Hill
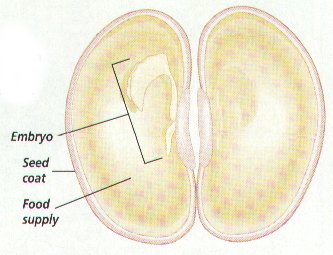
Reproductive Adaptations:
Copyright Holt, Rinehart, & Winston
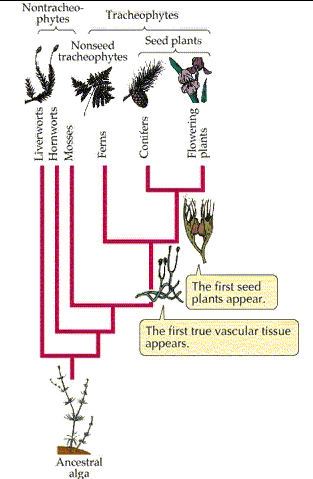
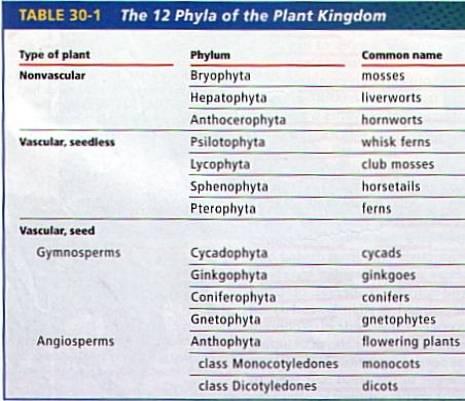
Classification of Plants:
Copyright Holt, Rinehart, & Winston


Plant Life Cycles:
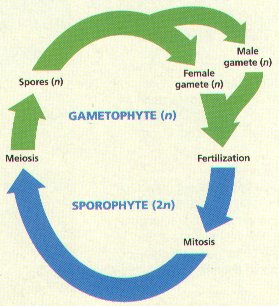
Copyright Holt, Rinehart, & Winston

Seed-Bearing, Vascular Plants:

Gymnosperms:
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Cycad | Welwitshcia (gnetophyte) |
Gingko | Fir Tree (Conifer) |
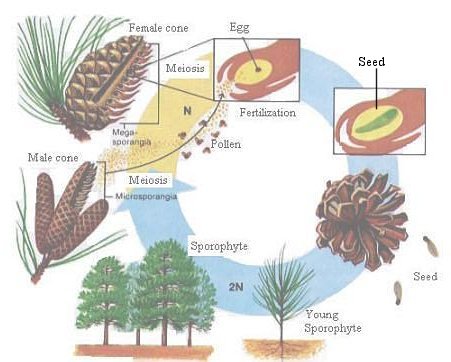
Division Cycadophyta:

Zamia (native to Georgia)
Division Gingkophyta:

Division Coniferophyta:
 |
 |
| Pollen Cone | Seed Cone |
 |
 |
| Redwood Tree | Bristlecone pine Tree |
Division Gnetophyta:
 |
 |
| Welwitshcia | Ephedra |
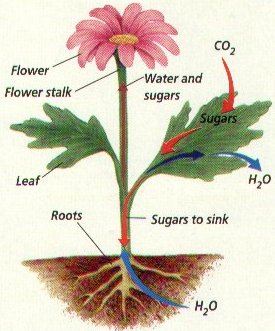
Division Anthophyta (Angiosperms):



| Cell Cycle & Cell Division Review |  |
1. Chromosomes are Rod Shaped structures made of _________ and ___________.
2. State the cell theory.
3. The phases in the life of a cell are called the ______________ _____________.
4. The cell cycle consists of ________, __________, __________, & division.
5. ________________ is a series of ______________ in cell division during which the _____________________ of a cell divides into __________ __________ with ____________ _____________ material.
6. _________________ only occurs in _________________________ cells.
7. The period of cell growth prior to division is _________________________.
8. Interphase consist of what three phases and describe each:
a.
b.
c.
9. The period during which DNA is copied ______________________.
10. DNA replication in a cell results in _________________ ____________________.
11. Replication is the process of copying _______________ ____________________.
12. Cell division is the process by which one _________ produces __________ new identical _________ ___________.
13. Cell division involves 2 Steps called __________________ _____________ ________________________.
The steps are:
a.
b.
14. Step 1 of cell division is called ___________, and step 2 is called ______________.
15. During __________the cytoplasm of the cell divides into _______ new cells called ___________ ___________.
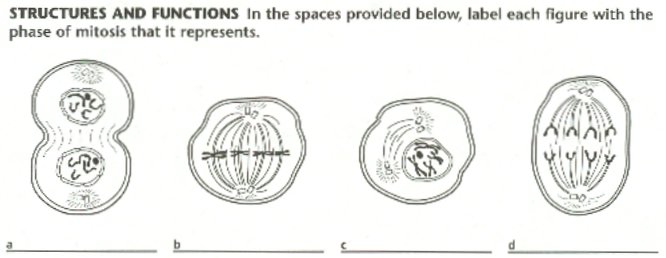
16. The steps or phases of Mitosis are ___________, ____________, ____________, and ________________.
17. _________ is the process by which a nucleus gives rise to ___________ _________ _____________.
18. In anaphase, the sister Chromatids __________________________________.
19. The cell is pinched into two and cytokinesis begins during ____________________.
20. The assembling of microtubules that make up the spindle fibers occurs during _____________.
21. During prophase the _________ and ________ ____________ disappear.
22. The center of the cell is called the ___________ _______________.
23. ________________ condenses into chromosomes of two _________________ ____________________, joined together by the _____________________ during __________________________.
24. The production of offspring from one parent is called ________________________ ________________________.
25. During mitosis, centrioles are present only in _________________________ cells.
26. Most organisms are capable of combining ______________________ from two parents to produce ______________________.
27. The phase of mitosis during which chromosomes move to opposite poles is called ____________________________________.
28. When chromosomes of two parents combined to produce offspring, the process is known as _____________________ _____________________.
29. The chromosomes that combine during sexual reproduction are contained in special reproductive cells called _________________________.
30. In most organisms, ________________ can be either _____________ or _________________.
31. Eggs are _______________ than sperm, but are ______________________.
32. Sperm have ______________________ that help them swim to the ___________.
33. Gametes are formed by _______________________, a type of nuclear division in which _____________________ number is ______________________ and is followed by ________________ ______________________.
34. In humans, specialized reproductive cells with _________ chromosomes, called ____________________ cells, undergo ________________ and ___________ ________________ to give rise to egg or sperm that have only _______ chromosomes, ___________________ cells.
35. Any cell that contains two complete sets of chromosomes is called a _____________________ ______________.
36. A cell with only one complete set of chromosomes is called a ____________________ ______________.
37. When an egg and sperm join to produce a new individual, the process is called _________________________________.
38. The single cell that results from fertilization is called a ____________________.
39. Matching pairs of chromosomes in a diploid cell are called ___________________ _________________.
40. During ______________________, the cytoplasm of a cell and its organelles separate into two New ______________________ _____________.
41. Cytokinesis proceeds differently in animal and plant cells. In animal cells, the cytoplasm divides when a _______________ called the ________________ _________________ forms through the middle of the parent cell. In a plant cell, the material form a ______________ ____________ and __________________ gather and fuse along the equator or middle of the cell.
42. The term cleavage furrow refers to _______________________________________
________________________________________________.
43. The exchange of genes between pairs of homologous chromosomes is called _____________________ – ___________________________ and Only occurs during __________________________________ of meiosis.
44. What equally divides chromatids between offspring cells _________________ ____________________.
45. The time between cell division is called ________________________________.
46. The division of a prokaryotic cell into two offspring cells is called _______________________ ____________________________.
47. What equally divides an animal cell into two offspring cells (daughter cells) ________________________ _______________________.
48. Each protein in an organisms DNA is coded for an individual __________________.
49. If an organism has 12 chromosomes in each body cell, how many chromosomes would you expect to find in the organism’s gametes? _________________
50. During which phase of meiosis do tetrads form? ___________________________
51. The division of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is called _________________________________.
52. What event occurs during synapsis? ______________________ __________ ___________________________ _______________________.
53. During mitosis and meiosis, kinetochore fibers are thought to move __________________________________.
54. Histones are proteins that _______________ in the _______________ of __________________ in eukaryotic cells.
55. Spermatogenesis results in _______________ _______________ cells.
56. Each offspring cell produced by binary fission contains an ____________________ __________________ of the original cell’s __________________________.
57. Crossing-over results in genetic recombination by permitting the ________________________ of genetic material between ____________________ and _______________________ chromosomes.
58. Two of the 46 human chromosomes are called _______________ _________________________, all others (44) are called _________________________.
59. The production of eggs is called ____________________________.
60. What structure not found in animal cells forms along the midline of a dividing plant cell? _________________________ ____________________________.
Answer the Following questions in paragraph form:
1. What is Cytokinesis? How is it different in plant and animal cells?
2. Explain the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis?
3. What is the Difference (Contrast) between Sex Chromosomes and Autosomes?
4. List 2 ways that meiosis differs from mitosis.
5. Compare the structure of a prokaryotic chromosome with that of eukaryotic chromosomes.
6. What are homologous chromosomes?
7. Explain the difference between a haploid cell and a diploid cell?
8. What is your diploid and haploid Number?
9. What is DNA? What are histones?
10. What is independent assortment, and how does it affect the genetic makeup of offspring cells?
11. What are chromatids and what holds two chromatids together?
12. Describe how you could determine if a dividing cell is a prokaryote or an eukaryote. What structures would you look for?
13. Compare the products of mitosis with those of meiosis II.
14. Describe the events of binary fission and what kind of organisms would use this.
15. What is the cell cycle?
16. How do the products of spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ?
17. What is interphase? What makes up and occurs during each part of interphase?
18. What is mitosis and in order, What are the four phases of mitosis?
19. What are kinetochore fibers and polar fibers? What are their functions?
20. Explain crossing-over, What is it? When does it occur? Why is it Important?
21. In what type of cell, Eukaryote, Prokaryote, or Both, does mitosis occur?
__________________________________________. EXPLAIN WHY?
22. Explain the difference between Mitosis and Cytokinesis.
23. What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction? Which has evolutionary value? Why?