| Bacteria Review |  |
1. The most numerous organisms on Earth are ____________________________________.
2. Type of bacteria that peptidoglycan is absent in cell walls _____________________________________________.
3. Type of bacteria that obtain energy from inorganic substances are __________________________________ _________________________________.
4. Type of bacteria that obtain nutrients from dead organisms ____________________________ ______________________________________.
5. Organisms that lack a cell nucleus are called ______________________________.
6. Most prokaryotes are __________________________________organisms.
7. Almost all prokaryotes are ____________________ than the smallest Eukaryotes.
8. Prokaryotes have _____________________________ that are different from those of Eukaryotes.
9. The bacteria can be divided into two Kingdoms: ______________________________ and
____________________________________________.
10. The ______________________________________ are a group of bacteria that live in Harsh Environments.
11. The prefix “ARCHEA” means ___________________________________.
12. Archaebacteria can be divided into Three Groups. LIST AND DESCRIBE EACH GROUP:
A. _____________________ ____________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
B. _____________________ ____________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
C. _____________________ ____________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
13. The Archaebacteria that produce methane are called _______________________________.
14. Archaebacteria that thrive in very salty conditions, such as the Dead Sea, are called
________________________________ ______________________________.
15. Archaebacteria that can live in extremely hot or acidic water are called ______________________________________________________.
16. The prefix “EU” means _________________________.
17. What is the important tool used for classifying Eubacteria called ________________________ ____________________________.
18. During Gram Staining, depending on structure of their __________ ____________, the
bacteria’s cell walls absorbs either the _______________ or ________________dye.
19.Those bacteria that take on the purple color are called _________________
_________________________ ___________________________
20. Gram-positive Bacteria used to make antibiotics are called __________________________________.
21. Gram-positive bacteria cause many diseases in humans by producing _________________________
which are poisons to our bodies.
22. Bacteria that appear Pink after staining are called _______________
________________________ ___________________________.
23. Gram-negative bacteria have an extra layer of ________________ on the outside
of the ____________ ____________ and appear ___________ after the Gram staining.
24. The lipid layer _______________ the purple stain from entering the cell wall.
25. Gram-negative bacteria do absorb the ____________ stain during the Gram-staining.
26. The extra layer of lipids also stops many ________________________ from entering the bacteria.
27. Scientist think that gram-negative bacteria may have evolved from a
____________________________ _____________________________.
28. ______________________ grow in the root nodules of such plants as soybean, clover, and alfalfa.
29. Rhizobacteria fix ______________________ from the atmosphere into a form that plants
and animals can use (this greatly helps both plants and animals). They convert the gaseous
nitrogen into compounds such as __________________________ (NH3).
30. Gram-negative bacteria are distinguished by an extra layer of _________________.
31. _______________________ are Gram-negative bacteria that perform plant-like
____________________________ and release oxygen as a by-product.
32. _____________________________ are much _________________ than many other
prokaryotes.
33. Organisms that obtain energy from oxidizing inorganic compound instead of sunlight are called _________________________________.
34. Whiplike structures used by bacteria for movements are called ______________________.
35. Photoautotrophs are bacteria that use ______________________ as an energy source.
36. Bacteria can be one of three different shapes:
A. _____________________________________________(Rod)
B. _____________________________________________(Sphere)
C. _____________________________________________(Spiral)
37. Bacteria usually gain part of their ____________________ from their shape.
38. Two major differences between groups of bacteria are their source of ____________________
and weather or not they use ________________ for cellular respiration.
39. Most bacteria are _______________________; they get their energy by consuming (eating) organic molecules.
40. Some are __________________ that make their own food from ________________.
41. ____________________________ obtain their food from inorganic compound instead of sunlight.
42. _________________________ use sunlight for energy.
43. Organisms that use oxygen during cellular respiration are called ________________ Organisms
that do not use oxygen are called __________________________. Typically they get their energy through _________________________________.
44. Bacteria called ______________ __________________ cannot live without oxygen.
45. Bacteria called ____________ _______________ cannot live in the presence of oxygen.
46. Bacteria called ________________ __________________ can use oxygen when it is available,
but do not depend on it.
47. Most bacteria reproduce by a process called _________________ __________________.
48. Binary fission is a process in which the __________________________ replicate,
after which the ________________ divides.
49. Binary fission is a type of _____________________ reproduction.
50. Some bacteria contain smaller pieces of circular DNA called ________________________.
51. Bacteria can exchange genes by one of three special means: _________________________, __________________________, or _____________________________.
52. The process of exchanging genetic material through cell to cell contact is called
___________________________________.
53. Hair like structures on the surface of bacteria are called ______________________.
54. The process by which bacteria cells pick up and incorporate DNA from dead bacteria cells is called _________________________________.
55. Using a virus to transfer DNA from one bacterial cell to another is called _____________________________.
56. When living conditions become _____________________, some bacteria from special
dehydrated cells called ___________________________________.
57. Bacteria that form ___________________ have an advantage for ____________________.
58. Bacteria the feed on and that break down dead organic material are called ______________________________.
59. Type of bacteria that produces many antibiotics__________________________.
60. Type of bacteria that produces endotoxins ___________________________ ___________________________.
61. Bacteria that can only survive in the absence of oxygen are called _______________________ ____________________________.
62. Gram-negative bacteria appear ________________ when they undergo the Gram-stain procedure.
63. Type of bacteria that performs nitrogen fixation is _________________________.
64. Type of bacteria that peptidoglycan is present in cell walls _________________________________.
65. What bacteria are thought to be responsible for establishing the Earth’s oxygen-rich atmosphere? ____________________________________
66. Bacteria cells typically lack ____________________________________.
67. Bacterial disease of the intestines are usually transmitted by contaminated __________________________ or __________________________.
68. What are the Three Mechanism of action of an antibiotic?
DIRECTIONS: Answer the questions below as completely and as thoroughly as possible. Answer the question in essay form (not outline form), using complete sentences. You may use diagrams to supplement your answers, but a diagram alone without appropriate discussion is inadequate.
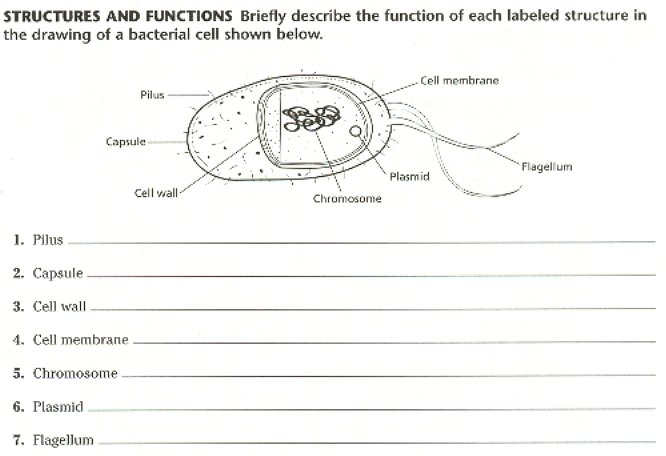
1. Describe the capsule of a bacterium and its function.
2. Identify the most common shapes of Eubacteria and Describe each.
3. Compare and Contrast Archaebacteria with Eubacteria.
4. Identify Three Ways that bacteria are used to produce substances for human use.
5. Describe the significance of cyanobacteria in the formation of the Earth’s atmosphere.
6. List the various structures of the bacterial cell, and Describe their function.
7. Explain the laboratory technique Gram stain and Explain what it is used for.
8. Define the term genetic recombination as it applies to bacteria, and Describe Three ways that genetic
recombination occurs in bacteria.
9. Explain how chemoautotrophs differ from photosynthetic autotrophs.
10. Explain how the terms bacteria, Eubacteria, and Archaebacteria, relate to one another.
11. Describe Three Types of movement among bacteria.
12. List the characteristics that are used to classify bacteria.
13. Explain how chemoautotrophs harvest energy from the environment.
14. Describe Two Ways bacteria cause disease.
15. Explain why antibiotic resistance among bacteria is increasing.
16. List one distinguishing characteristic of each of the three main groups of Archaebacteria.