|
Scientific Equipment All Materials © Cmassengale
|
|||
|
|
|||
 |
Compound Light Microscope (LM)-used to enlarge an image | Graduated Cylinder – used to measure the volume of liquids | |
 |
Microscope Slide – supports an item being examined under the microscope |  |
Cover slip – covers specimen on a slide |
 |
Beaker – holds liquids while they are being stirred or heated | Test Tube Brush – used to clean test tubes | |
 |
Evaporating Dish – used for heating solids |  |
Pinch Clamps – used to control the flow of liquids through tubing |
 |
Funnel – assists in transferring liquids to containers with smaller openings | Striker – used to ignite a burner | |
 |
Test Tubes – holds liquids for observation or testing |  |
Safety goggles – protects the eyes from damaging substances |
| Pipet pump – dispenses known volumes of liquids | Eyedropper – used to transfer small amounts of liquids | ||
 |
Forceps – used to hold or lift specimens |  |
Magnifying glass – enlarges the image of an object |
 |
Crucible – containers used for “strong” heating | Test Tube Rack – holds test tubes during observation or testing | |
 |
Wash Bottle – used for rinsing solids out of a container | Pipet – used for exact measurements of liquids | |
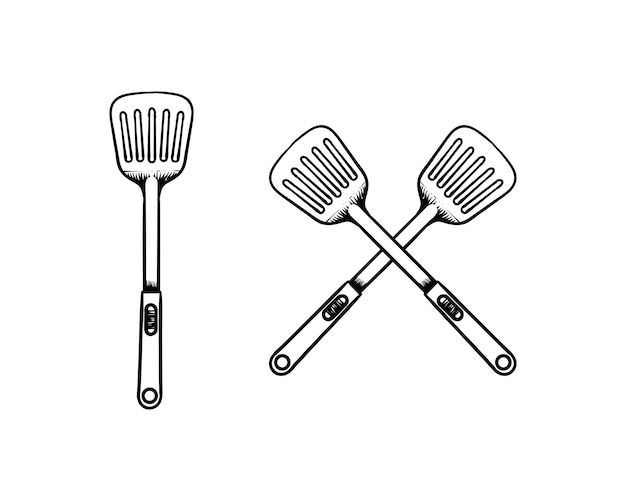 |
Spatula – chemical spoons used to transfer solids from their original container to a scale for weighing |  |
Wire Gauze – adds additional support for containers held on tripods or O-rings |
 |
Crucible Tongs – used for picking up crucibles & crucible covers only |  |
Mortar & Pestle – used to grind solids into powders |
 |
Florence Flask – used to store liquids |  |
Erlenmeyer Flask -used to store solutions |
 |
Dissecting Pan – holds specimen being dissected |  |
Test Tube Holder – holds test tubes while heating |
 |
Electronic Balance – used for weighing substances |  |
Bunsen Burner – heat source |
 |
Thermometer – used to measure temperature | Stopper – used to cap flasks containing liquids | |
 |
Scalpel – used for cutting specimens being dissected |  |
Tubing – hose used for connecting glassware |
 |
Petri Dish – plate used to culture microorganisms |  |
Triple Beam Balance – used for weighing substances |
 |
O-Ring – used with ring stands to support heated vessels | 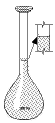 |
Volumetric Flask – used to mix precise volumes of liquids |
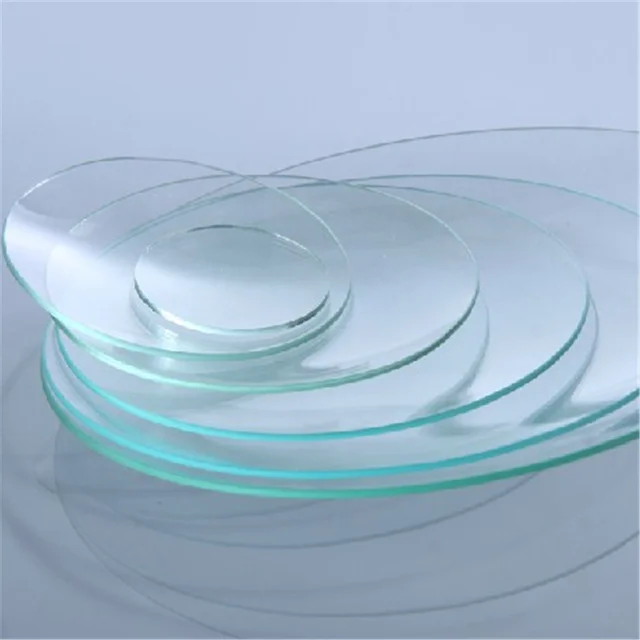 |
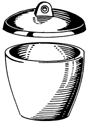
Watch Glass – used on top of beakers when heating | Desiccators – used to remove moisture from substances | |
| PRINT EQUIPMENT SHEET FOR NOTEBOOK | BACK | ||
