 CHAPTER 8, CELL REPRODUCTIONSECTION 8-1, CHROMOSOMES
CHAPTER 8, CELL REPRODUCTIONSECTION 8-1, CHROMOSOMES
DNA is a long thin molecule that stores Genetic Information. The DNA in a human cell is estimated to consist of six billion pairs of nucleotides.
OBJECTIVES: Describe the structure of a chromosome. Compare prokaryotic chromosomes with eukaryotic chromosomes. Explain the differences between sex chromosomes and autosomes. Give examples of diploid and haploid cells.
CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE
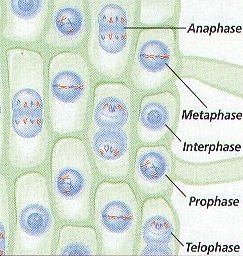
1. During Cell Division, the DNA (CHROMATIN) in an Eukaryotic Cell’s Nucleus is coiled into very tight compact structures called CHROMOSOMES.(Figure 8-1)
2. Chromosomes are Rod Shaped structures made of DNA and Proteins.
3. The Chromosomes of stained Eukaryotic cells undergoing cell division are visible as darkened structures inside the Nuclear Membrane.
4. The DNA in Eukaryotic cells wraps tightly around Proteins called HISTONES. They help to maintain the shape of Chromosomes and aid in the tight packing of DNA.
5. Proteins called NONHISTONE Proteins Do Not participate in packing of DNA, they are involved in Controlling the Activity of Specific Regions of the DNA.
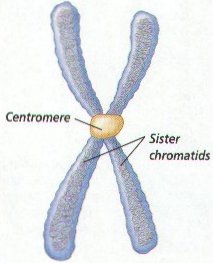 6. When preparing for Cell Division, Chromosomes form Copies of themselves, Each half of the Chromosome is called a CHROMATID or SISTER CHROMATIDS. Chromatids form as the DNA makes copies of itself before cell division. (Figure 8-2)
6. When preparing for Cell Division, Chromosomes form Copies of themselves, Each half of the Chromosome is called a CHROMATID or SISTER CHROMATIDS. Chromatids form as the DNA makes copies of itself before cell division. (Figure 8-2)
7. The constricted area of each Chromatid is called a CENTROMERE . The Centromere holds the Two Chromatids together until the separate during Cell Division.
8. Between Cell Division, DNA IS NOT so Tightly Coiled into Chromosomes. The Less tightly coiled DNA-Protein complex is called CHROMATIN .
9. Chromosomes are simpler in prokaryotes. The DNA of most Prokaryotes comprises only ONE Chromosome, which is attached to the inside of the Cell Membrane.
10. Prokaryotic Chromosomes consist of a circular DNA Molecule and associated Proteins.
CHROMOSOME NUMBERS
1. EACH HUMAN BODY CELL CONTAINS 46 CHROMOSOMES, (2n) OR TWO COMPLETE SETS.
2. ANY CELL THAT CONTAINS TWO COMPLETE SETS OF CHROMOSOMES IS CALLED A DIPLOID CELL. A Diploid Cell is commonly abbreviated as 2n.
3. THE NUMBER OF CHROMOSOMES IN A DIPLOID CELL IS CALLED THE DIPLOID NUMBER. EVERY ORGANISM HAS A CHARACTERISTIC DIPLOID NUMBER (2n).
4. EXAMPLES: FRUIT FLIES – 8, LETTUCE – 14, GOLDFISH 94, AND HUMANS 46.
5. A CELL WITH ONLY ONE COMPLETE SET OF CHROMOSOMES IS CALLED A HAPLOID CELL.
A Haploid Cell is abbreviated as 1n.
6. GAMETES, EGGS AND SPERM CONTAIN ONLY ONE COMPLETE SET. EACH HUMAN SPERM OR EGG (GAMETE) CONTAINS 23 CHROMOSOMES, THE HAPLOID NUMBER (1n) FOR ALL HUMANS.
7. WHEN AN EGG AND A SPERM OF THE SAME TYPE OF ORGANISM JOIN TO PRODUCE A NEW INDIVIDUAL, THE PROCESS IS CALLED FERTILIZATION.
8. THE SINGLE CELL THAT RESULTS FROM FERTILIZATION IS KNOWN AS A ZYGOTE. THE ZYGOTE CONTAINS TWO COMPLETE SETS OF CHROMOSOMES, ONE SET FROM EACH GAMETE, FORMING A DIPLOID CELL. IN MOST MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS, THE ZYGOTE IS THE FIRST CELL OF THE NEW INDIVIDUAL.
 9. The Chromosomes in the Zygote exist in PAIRS. For every Chromosome that was in the egg, there is a matching Chromosome from the sperm.
9. The Chromosomes in the Zygote exist in PAIRS. For every Chromosome that was in the egg, there is a matching Chromosome from the sperm.
10. Human and Animal Chromosomes are categorized as either SEX CHROMOSOMES or AUTOSOMES.
11. SEX CHROMOSOMES are Chromosomes that Determine the SEX of an Organism.
12. In Humans, Sex Chromosomes are either X or Y. Females have TWO X Chromosomes and Males have an X and Y Chromosome.
13. All the Other Chromosomes in an Organism are called AUTOSOMES.
14. TWO of the 46 Human Chromosomes are Sex Chromosomes, while the reaming 44 are Autosomes.
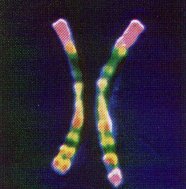 15. MATCH SET OF AUTOSOMES IN A DIPLOID CELL ARE CALLED HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS. BOTH CHROMOSOMES IN A HOMOLOGOUS PAIR CONTAIN INFORMATION THAT CODE THE SAME TRAIT (GENES). Example Eye Color.
15. MATCH SET OF AUTOSOMES IN A DIPLOID CELL ARE CALLED HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS. BOTH CHROMOSOMES IN A HOMOLOGOUS PAIR CONTAIN INFORMATION THAT CODE THE SAME TRAIT (GENES). Example Eye Color.
SECTION 8-2, CELL DIVISION
All cells are derived from preexisting cells. Cell division is the process by which cells produce offspring cells. Cell division differs in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In eukaryotes, cell division differs in different stages of an organisms life cycle.
OBJECTIVES: Describe the events of binary fission. Describe each phase of the cell cycle. Summarize the phases of mitosis. Compare cytokinesis in animal cells with cytokinesis in plant cells.
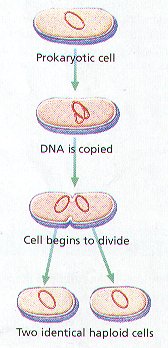 CELL DIVISION IN PROKARYOTES
CELL DIVISION IN PROKARYOTES
1. BINARY FISSION is the Division of a Prokaryotic cell INTO TWO Offspring Cells.
2. Binary Fission consist of THREE General Stages: (Figure 8-4):
STAGE 1 – The Chromosome, which is attached to the Inside of the Cell Membrane, makes a COPY of Itself, Resulting in Two Identical Chromosomes Attached to the Inside of the Inner Cell Membrane.
STAGE 2 – The Cell continues to grow until it reaches approximately TWICE its Normal Size. Then a CELL WALL Begins forms between the Two Chromosomes.
STAGE 3 – The Cell SPLITS into TWO NEW CELLS. Each New Cell contains on the Identical Chromosomes.
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES
1. The trillions of cells that make up your body came from just ONE ORIGINAL CALLED: A FERTILIZED EGG (Zygote). The Cell Theory states “CELLS COME ONLY FROM THE REPRODUCTION OF EXISTING CELLS” Chapter 4.
2. Each time A Cell Reproduces, the NEW Cells that are formed contained all the ESSENTIAL CYTOPLASM, ORGANELLES, AND NUCLEIC ACIDS NEEDED TO SURVIVE AND FUNCTION.
3. A Cell typically goes through PHASES during its Life, performing life processes of GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT before it divides into new cells.
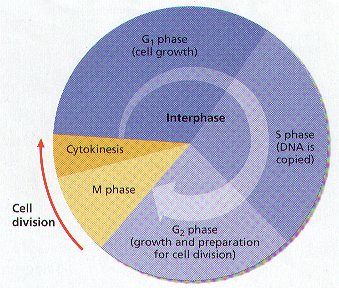 4. THE PHASES OF LIFE OF A CELL ARE CALLED THE CELL CYCLE . THE CELL CYCLE CONSISTS OF THREE PHASES:
4. THE PHASES OF LIFE OF A CELL ARE CALLED THE CELL CYCLE . THE CELL CYCLE CONSISTS OF THREE PHASES:
A. INTERPHASE
B. MITOSIS
C. CYTOKINESIS.
5. The CELL CYCLE is the Repeating Events that make up the Life of a Cell. (Figure 8-5)
6. Cell Division is One Phase of the Cell Cycle. Cell Division consists of MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS.
7. MITOSIS is a Series of PHASES in Cell Division during which the NUCLEUS of a Cell Divides into TWO NUCLEI WITH IDENTICAL GENETIC MATERIAL. MITOSIS OCCURS ONLY IN EUKARYOTES.
INTERPHASE
1. INTERPHASE IS THE PORTION OF THE CELL CYCLE BETWEEN DIVISION.
2. Interphase is the LONGEST Phase in the Cell Cycle of a typical Cell. Interphase used to be referred to as the “RESTING PHASE”.
3. During Interphase, calls carry on all their usual functions, such as respiration and enzyme production. The Cell also GROWS and DEVELOPS into MATURE FUNCTIONING Cells while in Interphase. It is the period of normal metabolic activity.
4. INTERPHASE CONSIST OF THREE PHASES:
A. G1 PHASE – PERIOD OF NORMAL METABOLIC CELLULAR ACTIVITIES: THE NUMBER OF ORGANELLES AND AMOUNT OF CYTOPLASM IN A CELL INCREASE. Offspring Cells Grow to Mature Size.
B. S PHASE – THE GENETIC MATERIAL (DNA) IS DUPLICATED (COPIED). THE CHROMOSOMES OF THE CELL REPLICATE.
C. G2 PHASE – Structure directly involved with mitosis are formed. The Cell makes the Organelles and substances it needs for Cell Division. A time during which the Cell prepares to divide.
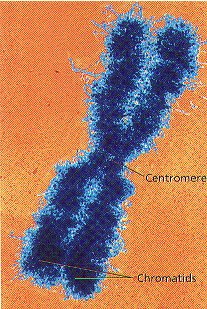 5. REPLICATION IS THE PROCESS OF COPYING GENETIC MATERIAL.
5. REPLICATION IS THE PROCESS OF COPYING GENETIC MATERIAL.
6. REPLICATION RESULTS IN TWO IDENTICAL COPIES OF A CHROMOSOME CALLED SISTER CHROMATIDS.
7. CHROMOSOMES MUST REPLICATE DURING INTERPHASE SO THERE WILL BE A COMPLETE COPY OF EACH CHROMOSOME IN EACH NEW CELL.
8. BECAUSE THE DNA CONTAINED IN CHROMOSOMES CONTROL GROWTH DEVELOPMENT, AND FUNCTION OF EVERY CELL, EACH NEW CELL MUST HAVE AN EXACT COPY OF THE ORIGINAL SET OF CHROMOSOMES.
CELL DIVISION
1. CELL DIVISION IS THE PROCESS BY WHICH ONE CELL PRODUCES TWO NEW IDENTICAL DAUGHTER CELLS.
2. CELL DIVISION INVOLVES TWO STEPS: CALLED MITOTIC CELL DIVISION.
A. MITOSIS – FIRST STEP. A SERIES OF PHASES IN CELL DIVISION DURING WHICH THE NUCLEUS OF A CELL DIVIDES INTO TWO NUCLEI WITH IDENTICAL GENETIC MATERIAL.
B. CYTOKINESIS – SECOND STEP. THE CYTOPLASM OF THE CELL DIVIDES INTO TWO NEW CELLS CALLED DAUGHTER CELLS.
3. DAUGHTER CELL NUCLEI ARE IDENTICAL TO THE PARENT CELL NUCLEUS IN EVERY WAY. LIKE THEIR PARENT CELL, SOME DAUGHTER CELLS WILL PASS THROUGH THE CELL CYCLE OF GROWTH, DEVELOPMENT, AND CELL DIVISION.
4. MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS GROW AS MORE CELLS REPEAT THE CYCLE OF CELL DIVISION AND GROWTH.
MITOSIS
1. Mitosis is the Division of the Nucleus, which occurs during Cell Division.
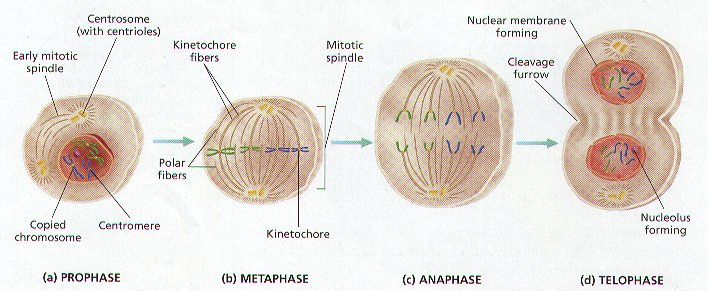
2. Biologist have named the Steps, or Phases, of Mitosis to help study the process. The FOUR Phases of Mitosis are called PROPHASE, METAPHASE, ANAPHASE, AND TELOPHASE. (Figure 8-6)
3. THE ACTUALLY PROCESS OF MITOSIS IS CONTINUOUS.
4. MITOSIS IS THE PROCESS BY WHICH A NUCLEUS GIVES RISE TO TWO IDENTICAL NUCLEI.
5. INTERPHASE PRIOR TO MITOSIS, THE PERIOD OF NORMAL METABOLIC ACTIVITY. The Chromosomes REPLICATE and the CYTOPLASM Increases as he cell prepares to divide. Interphase includes G1, S, G2 Phases of the Cell Cycle.
FOUR PHASES OF MITOSIS
PHASE 1- PROPHASE (Figure 8-6 (a))
1. Chromatin condenses into Chromosomes of TWO Sister Chromatids joined together by the CENTROMERE, and visible when viewed through a microscope.
2. THE NUCLEOLUS AND NUCLEAR MEMBRANE DISAPPEAR.
3. TWO Structures called CENTROSOMES appear next to the Disappearing Nucleus. In Animal Cells, each Centrosome contains a pair of small, cylindrical bodies called CENTRIOLES. Plant Cells lack Centrioles.
4. In BOTH Animal and Plant Cells, the Centrosomes move toward opposite poles of the cell. As they Separate, SPINDLE FIBERS made of microtubules radiate from the Centrosomes in preparation for Mitosis. The array of Spindle fibers is called the MITOTIC SPINDLE, which serves to Equally divides the Sister Chromatids between the Two Offspring Cells.
5. There are TWO Type of Spindle Fibers:
A. KINETOCHORE FIBERS – They Attached to the Centromere Region of each Sister Chromatids.
B. POLAR FIBERS – they extend across the dividing cell from Centrosome to Centrosome.
PHASE 2 – METAPHASE (Figure 8-6 (b))
1. The Chromosomes are moved to the CENTER of the CELL (Equatorial Plane) by the Kinetochore Fibers attached to the Centromeres.
2. The Two Sister Chromatids of each Chromosome are attached to Kinetochore Fibers radiating from OPPOSITE ENDS OF THE CELL.
PHASE 3 – ANAPHASE (Figure 8-6 (c))
1. The Centromeres of Each Chromosome are pulled by the Kinetochore Fibers toward the ends of the cell (OPPOSITE POLES).
2. THE SISTER CHROMATIDS ARE THUS SEPARATED FROM EACH OTHER. They are now Considered to be Individual Chromosomes.
PHASE 4 – TELOPHASE (Figure 8-6 (d))
1. After the Chromosomes reach opposite ends of the Cell, the Spindle Fibers Disassemble.
2. The Chromosomes return to less tightly coiled Chromatin State.
3. New Nuclear Envelope begins to form around the Chromosomes at each end of the cell.
4. CYTOKINESIS BEGINS.
5. THE PROCESS OF MITOSIS IS NOW COMPLETE. THE CELL MEMBRANE BEGINS TO PINCH THE CELL IN TWO AS CYTOKINESIS BEGINS.
CYTOKINESIS
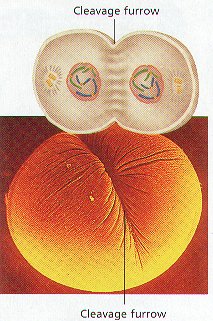 1. Following the last phase of Mitosis, Cytokinesis COMPLETES the process of Cell Division.
1. Following the last phase of Mitosis, Cytokinesis COMPLETES the process of Cell Division.
2. During Cytokinesis, the Cytoplasm of a cell and its ORGANELLES SEPARATE INTO TWO NEW DAUGHTER CELLS.
3. Cytokinesis proceeds differently in animal and plant cells.
4. CYTOKINESIS OF ANIMAL CELLS: The Cytoplasm Divides when a GROOVE called the CLEAVAGE FURROW forms through the Middle of the Parent Cell. The Cleavage Furrow Deepens until the parent cell pinches into TWO New Identical Cells. The New Cells are Now in INTERPHASE.
5. CYTOKINESIS OF PLANT CELLS: In a Plant Cell, the material for NEW CELL WALL CALLED THE CELL PLATE AND MEMBRANES GATHER AND FUSE ALONG THE EQUATOR, OR MIDDLE OF THE CELL, BETWEEN TWO NUCLEI. Forming TWO New Identical Cells.
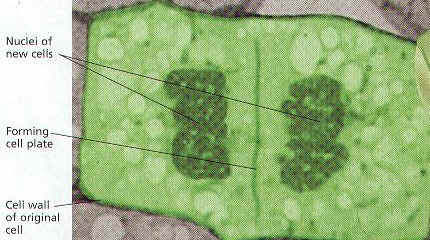
6. In Both Animal and Plant Cells, New Offspring Cells are approximately equal in Size.
SECTION 8-3, MEIOSIS
Meiosis is a process of nuclear division that Reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to Half the number in the original cell. The Halving of the chromosome number counteracts a fusion of cells later in the life cycle of the organism. For example, in humans, meiosis produces haploid reproductive cells called GAMETES. Human gametes are sperm and egg cells, each which contains 23(1n) chromosomes. The fusion of sperm and egg results in a zygote that contains 46 (2n) chromosomes.
OBJECTIVES: List and describe the phases of meiosis. Compare the end products of mitosis with those of meiosis. Explain crossing-over and how it contributes to the production of unique individuals. Summarize the major characteristics of spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
1. Most organisms are capable of COMBINING CHROMOSOMES FROM TWO PARENTS TO PRODUCE OFFSPRING.
2. WHEN CHROMOSOMES OF TWO PARENTS COMBINE TO PRODUCE OFFSPRING, THE PROCESS IS KNOWN As SEXUAL REPRODUCTION.
3. THE CHROMOSOMES THAT COMBINE DURING SEXUAL REPRODUCTION ARE CONTAINED IN SPECIAL REPRODUCTIVE CELLS CALLED GAMETES.
4. IN MOST ORGANISMS, GAMETES CAN BE EITHER EGG OR SPERM .
5. EGGS are larger than sperm and contain a lot of Cytoplasm. An egg is nonmotile.
6. SPERM Cells contain very little Cytoplasm, have Flagella, that helps them swim to the nonmotile egg.
7. The Chromosomes of Two Gametes are added together when they join. The number of Chromosomes in the offspring DOES NOT DOUBLE WITH EACH GENERATION, BUT REMAINS THE SAME BECAUSE OF MEIOSIS.
8. MEIOSIS IS THE WAY MANY ORGANISMS PRODUCE GAMETES THROUGH A TYPE OF CELL REPRODUCTION.
9. MEIOSIS IS A TYPE OF NUCLEAR DIVISION IN WHICH THE CHROMOSOME NUMBER IS HALVED. LIKE MITOSIS, MEIOSIS IS FOLLOWED BY CYTOKINESIS.
10. IN HUMANS SPECIALIZED REPRODUCTIVE CELLS WITH 46 CHROMOSOMES (2n) (DIPLOID CELL) UNDERGO MEIOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS TO GIVE RISE TO EGG OR SPERM THAT HAVE ONLY 23 CHROMOSOMES (1N) (HAPLOID CELL) EACH.
11. MEIOSIS ONLY OCCURS IN EUKARYOTIC CELLS IN PHASES SIMILAR TO THE PHASES OF MITOSIS.
12. MEIOSIS IS DIFFERENT FROM MITOSIS IN SOME VERY IMPORTANT WAYS.
A. The process of meiosis results in the production of Daughter Cells that have HALF THE NUMBER OF CHROMOSOMES OF THE PARENT CELL (HAPLOID CELL).
B. Daughter Cell produced by meiosis ARE NOT ALL ALIKE. THE DAUGHTER CELLS MAY HAVE DIFFERENT CHROMOSOMES FROM EACH OTHER.
C. The NUMBER OF CELLS PRODUCED BY MEIOSIS IS DIFFERENT.
(1) Mitosis – One Parent Cell PRODUCES TWO DIPLOID DAUGHTER CELLS.
(2) Meiosis – One Parent Cell PRODUCES FOUR HAPLOID DAUGHTER CELLS.
STAGES OF MEIOSIS
1. THE PROCESS OF MEIOSIS SEPARATES THE PAIRS OF CHROMOSOMES IN A DIPLOID CELL TO FORM HAPLOID CELLS.
2. ONE PARENT CELL DIVIDES TWICE TO PRODUCE FOUR HAPLOID DAUGHTER CELLS.
3. DURING MEIOSIS, THE NUMBER OF CHROMOSOMES IN EACH CELL IS REDUCED FROM DIPLOID TO HAPLOID BY SEPARATING HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS OF CHROMOSOMES.
4. MEIOSIS PROCEEDS IN TWO MAIN STAGES:
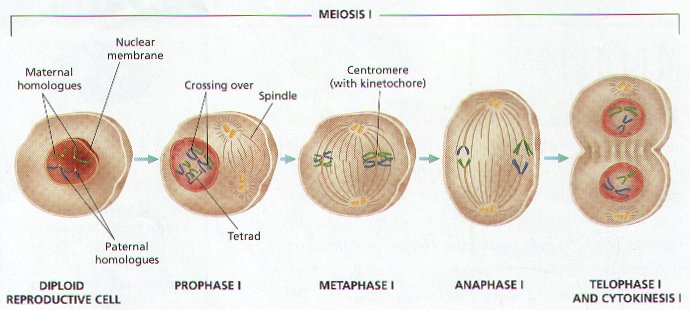
A. MEIOSIS I HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS ARE SEPARATED.
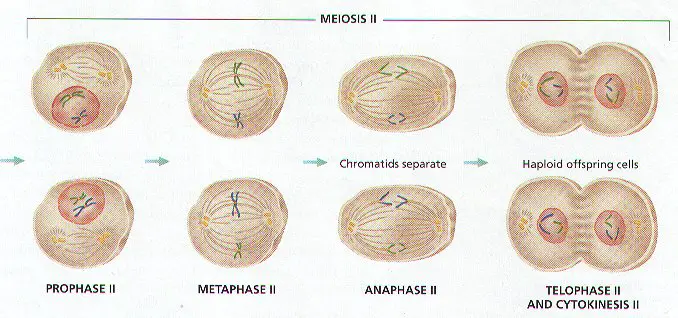
B. MEIOSIS II THE SISTER CHROMATIDS OF EACH CHROMOSOME ARE SEPARATED.
MEIOSIS I (Figure 8-9)
1. AT THE START OF MEIOSIS I EACH CHROMOSOME CONSIST OF TWO STRANDS OF SISTER CHROMATIDS CONNECTED AT THE CENTROMERE.
2. HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS OF CHROMOSOMES COME TOGETHER BEFORE MEIOSIS BEGINS, AN EVENT THAT DOES NOT OCCUR IN MITOSIS. THIS EVENT IS CALLED SYNAPSIS .
3. Each Pair of Homologous Chromosomes is called a TETRAD .
PROPHASE I.
1. Chromosomes become thick and visible, the chromosomes of each homologous pair are tangled together.
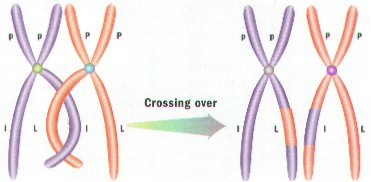
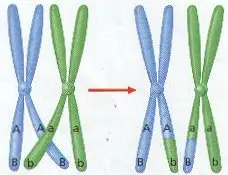 2. Portions of Chromatids may Break Off and attach to Adjacent Chromatids on the homologous Chromosome – a process called CROSSING-OVER. (Figure 8-10)
2. Portions of Chromatids may Break Off and attach to Adjacent Chromatids on the homologous Chromosome – a process called CROSSING-OVER. (Figure 8-10)
3. Crossing-Over results in Genetic Recombination by producing a New Mixture of Genetic Material.
4. Each pair consists of FOUR CHROMATIDS, BECAUSE EACH CHROMOSOME IN THE PAIR HAD REPLICATED BEFORE MEIOSIS BEGAN.
5. The Nucleoli and the Nuclear Envelope disappear and the spindle fibers form.
METAPHASE I. Homologous pairs (Tetrads) are still together and arrange in the middle of the cell.
ANAPHASE I. The homologous pairs of chromosomes separate from each other, spindle fibers pull one member from each pair to opposite ends of the cell. The Random separation of the Homologous Chromosomes is called INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT.
TELOPHASE I. Cytokinesis takes place; each new cell is haploid, containing one chromosome
from each pair.
MEIOSIS II (Figure 8-11)
1. CHROMOSOMES DO NOT REPLICATE BEFORE BEGINNING THE SECOND PHASE MEIOSIS II WILL DIVIDE CHROMOSOMES INTO HAPLOID CELLS CALLED GAMETES.
2. Each Diploid Cell from Meiosis I will go through a second division, forming the FOUR GAMETES HAPLOID CELL. (Review Figure 8-11)
CROSSING-OVER
 1. CHROMOSOMES OF ALL ORGANISMS CONTAIN REGIONS CALLED GENES .
1. CHROMOSOMES OF ALL ORGANISMS CONTAIN REGIONS CALLED GENES .
2. EACH GENE CODES FOR ONE TRAIT, OR CHARACTERISTIC, OF THE ORGANISM.
3. ONE VERY IMPORTANT EVENT THAT CAN OCCUR DURING MEIOSIS I IS CROSSING- OVER.
4. CROSSING-OVER IS THE EXCHANGE OF GENES BETWEEN PAIR OF HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES.
5. CROSSING-OVER OCCURS ONLY DURING PROPHASE I (ONLY!) WHEN HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS ARE STILL JOINED TOGETHER. THESE PAIRS CAN SOMETIMES BREAK WHERE THEY MEET AN EXCHANGE GENES. (Figure 8-10)
FORMATION OF GAMETES
 1. In Animals, meiosis produces haploid reproductive cells called GAMETES.
1. In Animals, meiosis produces haploid reproductive cells called GAMETES.
2. Meiosis occurs within the Reproductive Organs, in the TESTES or OVARIES.
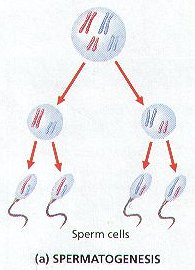
3. In the Testes, meiosis is involved in the production of Male Gametes known as Sperm Cells or Spermatozoa.
4. In the development of Sperm Cells, a Diploid Reproductive Cell divides Meiotically to form FOUR Haploid Cells called SPERMATIDS.
5. Each Spermatid then develops into a Mature Sperm Cell.
6. The production of Sperm Cells is called SPERMATOGENESIS . (Figure 8-12 (b))
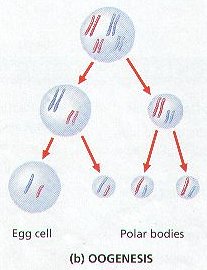 7. OOGENESIS is the production of Mature Egg Cells or OVA. (Figure 8-12 (c))
7. OOGENESIS is the production of Mature Egg Cells or OVA. (Figure 8-12 (c))
8. Notice that the Female only produces ONE EGG (OVUM) under normal circumstances.
9. Although creating 4 Haploid Cells through meiosis, only One Becomes the Egg, the other Three products of meiosis are called POLAR BODIES ,and Degenerate. This is due to the unequal dividing of the cytoplasm during Cytokinesis I & II.
ASEXUAL AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
1. EVOLUTION IS THE PROCESS OF CHANGE IN LIVING POPULATIONS OVER TIME.
2. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION is the production of Offspring from ONE PARENT.
3. Asexual reproduction DOES NOT Usually involve Meiosis or the Union of Gametes.
4. In Unicellular Organisms, such as bacteria, New Organisms are created by either BINARY FISSION or MITOSIS.
5. Asexual Reproduction in multicellular organisms results from BUDDING OFF a Portion of Their Bodies. (Plants)
6. The Offspring From Asexual Reproduction are Genetically Identical to the Parent.
7. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION is the Production of Offspring through Meiosis and the Union of a Sperm and an Egg.
8. MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION RESULTS IN NEW COMBINATIONS OF CHARACTERISTICS WITHIN A POPULATION.
9. ORGANISMS IN A POPULATION THAT REPRODUCE SEXUALLY ARE NOT ALL ALIKE.
10. DIFFERENCES AMONG MEMBERS OF A POPULATION ARE COLLECTIVELY CALLED VARIATION. WHICH RESULTS FROM THE RECOMBINATION OF GENES DURING MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION.
11. MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION SHUFFLE THE GENES FROM PARENT ORGANISMS, PRODUCING NEW COMBINATIONS OF GENES IN THE OFFSPRING.
12. AN ORGANISMS CHARACTERISTICS ENABLE IT TO SURVIVE IN IT’S ENVIRONMENT. THE CONDITIONS OF THE ENVIRONMENT DETERMINE WHICH CHARACTERISTICS OR TRAITS BENEFIT THE SURVIVAL AND WHICH DO NOT.
13. THE ORGANISMS WITH THE TRAITS TO SURVIVE WILL THEN REPRODUCE TO PASS THOSE POSITIVE TRAITS ON TO THEIR OFFSPRING.
14. OVER TIME THIS PROCESS LEADS TO THE CHANGE IN THE POPULATIONS, BECAUSE ONLY THOSE WITH POSITIVE TRAITS TO PASS ON WILL REPRODUCE. NATURAL SELECTION.
15. THE ACCUMULATION OF SUCH GENES AND TRAITS IN EACH GENERATION IS THE BASIS OF EVOLUTION.
16. SINCE ASEXUAL OFFSPRING HAVE THE EXACT SAME GENES AND TRAITS AS THE PARENT, GENETIC VARIATION RARELY OCCURS.
17. A CHANGE IN THE ENVIRONMENT THAT CAN DESTROY ONE INDIVIDUAL COULD DESTROY THE ENTIRE POPULATION.


 Birds & Mammals Study Guide
Birds & Mammals Study Guide